"Buy zestril 2.5mg visa, heart attack risk factors".
By: K. Mezir, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine
But hypertension in 9th month of pregnancy purchase zestril 5mg, it causes generation of action potential in nerve fibers distributed to hair cells arteria 3d medieval village buy zestril pills in toronto. Depolarization of hair cells causes them to release a neurotransmitter blood pressure exercise program buy zestril uk, which generates the action potential in the nerve fibers heart attack zippo lighter zestril 2.5 mg on-line. Movement of stereocilia in the opposite direction (away from kinocilium) causes hyperpolarization of hair cells. Hyperpolarization in hair cells stops generation of action potential in the nerve fibers. Adaptation of Receptors in Semicircular Canal during Rotation Hair cells of crista ampullaris generate impulses even at rest. At the commencement of rotation, discharge of impulses reaches a higher frequency of 600 to 800 per minute, depending upon the speed of rotation. However, the rapid discharge of impulses lasts only for the first 20 to 25 seconds of rotation. Afterwards, even if rotation continues, the frequency of impulses falls back to the resting level. Cause for adaptation of receptor cells At the onset of rotation, endolymph inside the semicircular canal does not move along with semicircular canal because of inertia of the fluid. So semicircular canal moves leaving the endolymph behind, which is like moving in the opposite direction. It causes stimulation of hair cells but, after about 20 seconds due to the accumulation of endolymph, a pressure is developed in ampulla. Hair cells of crista ampullaris of vertical semicircular canals are stimulated during the rotation of head in anteroposterior or transverse axis. However, the mechanism involved is similar to that of the hair cells of crista ampullaris of horizontal canals. During activation, receptor potential develops in hair cell due to the influx of potassium and calcium ions. Receptor potential causes release of neurotransmitter from hair cell, which induces development of action potential in the afferent nerve fiber. It is due to the natural stimulatory effect of vestibular apparatus during rotational acceleration. Vestibulo-ocular reflex and nystagmus Nystagmus is a reflex phenomenon that occurs in order to maintain the visual fixation. Since the movements of eyeballs occur in response to stimulation of vestibular apparatus this reflex is called vestibulo-ocular reflex. Movement of eyeball during nystagmus Nystagmus has two components of movement, which occur alternately: 1. Slow component At the beginning of rotation, since eyes are fixed at a particular object (point), eyeballs rotate slowly in the direction opposite to that of rotation of the head. Quick component When the slow movement of eyeballs is limited, the eyeballs move to a new fixation point in the direction of rotation of head. Quick component of nystagmus is due to the activation of some centers in brainstem. Postrotatory nystagmus Nystagmus that occurs immediately after stoppage of rotation is called postrotatory nystagmus. It is due to movement of cupula in opposite direction caused by the endolymph, when rotation is stopped. Postrotatory nystagmus can be demonstrated by Barany chair (see below for details). Postrotatory Reactions After the end of rotatory movement, two reactions occur: 1. Feeling of rotation in the opposite direction When rotation in clockwise direction is stopped suddenly, endolymph moves in the direction of rotation in right horizontal semicircular canal although the semicircular canal stops moving. However, in the case of left horizontal semicircular canal, endolymph moves into ampulla. There, it pushes cupula towards the utricle and stimulates the hair cells in crista of left canal. Nystagmus in Pathological Conditions Nystagmus is very common in lesions of cerebellum and lesions of brainstem involving vestibular nuclei or vestibular nerve.
Adaptogen (Jiaogulan). Zestril.
- What other names is Jiaogulan known by?
- Dosing considerations for Jiaogulan.
- Reducing cholesterol levels.
- Regulating blood pressure, bronchitis, stomach disorders, ulcers, constipation, gallstones, obesity, cancer, diabetes, sleeplessness (insomnia), backache, pain, improving memory, improving heart function, and other conditions.
- What is Jiaogulan?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Jiaogulan work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96288
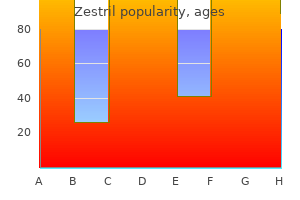
If the glenoid is well preserved hypertension 2013 guidelines buy 5 mg zestril fast delivery, a partial (hemi) joint replacement will also give good results blood pressure medication safe for pregnancy purchase zestril cheap. If the dislocation does not settle and recurs blood pressure normal numbers generic 2.5mg zestril with mastercard, then surgery to repair the Bankart lesion and reefing of the capsule will provide good results in over 90 per cent of cases heart attack xiami purchase zestril 10mg mastercard. A, B, D, E, H, J, K There are a large number of deformities associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Prosthetic replacement of the wrist is not currently proving as valuable in terms of pain relief and function as arthrodesis. Tendon repairs tend not to work well but tendon transfer using healthy tendons gives better results. It is the pattern of these three, the age and gender of the patient, and the cause of the onset of symptoms (traumatic or gradual) which give a clue to the diagnosis in most of the conditions. In the first instance, the treatment is physiotherapy to build the strength of the muscles around the shoulder. Repeated dislocations will need a surgical repair of the labrum and of the capsule. The woman who has fallen onto her shoulder (Scenario 7) will have suffered a fracture through osteoporotic bone. If, however, it is intra-articular or grossly displaced (so that the blood supply to the humeral head is damaged), a hemiarthroplasty may be the only option. If the intra-articular fracture is left (as used to happen), then traumatic osteoarthritis is inevitable in the years to come. This will present with gradual onset of pain, stiffness and weakness, and the best treatment is probably a shoulder replacement. Arthritis in the shoulder also develops in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and they too respond well to a shoulder replacement. The patient presenting with a painless but weak shoulder (Scenario 2) where the problem has developed over the years has almost certainly got a massive tear of the rotator cuff. The cuff has a poor blood supply and so any attempt at repair is doomed to failure. It may therefore be best to simply explain the diagnosis and commiserate with them. Once again, physiotherapy and re-education should be sufficient as the child will grow out of it if they stop doing it. The presentation of severe pain and stiffness after minor trauma (Scenario 3) is characteristic of a frozen shoulder. This is very slow to resolve and it is doubtful whether anything helps reduce the months of pain and stiffness, but most clinicians would offer analgesia and gentle physiotherapy. Severe pain and stiffness developing rapidly without any trauma at all (Scenario 3) could be a frozen shoulder but could also be calcifying tendinitis of the supraspinatus tendon. Frozen shoulder produces global pain and loss of movement, including pain on external rotation. On X-ray a calcific cloud will be visible in the supraspinatus tendon between the acromion and the humeral head. Painful arc syndrome is the finding that the patient cannot actively abduct their arm from their side beyond a certain point (the start of the painful arc) because it becomes very painful (Scenario 1). If, however, examiner lifts the arm for the patient through this painful arc, they are quite suddenly able to abduct the final bit without much pain. This condition can be diagnosed with an injection of local anaesthetic into the impinging area, and some attempt treatment with a steroid injection. However, trimming of the downward-pointing tip of the acromion (subacromial decompression) should relieve the impingement and therefore the pain. Elbow injury (a) 1A, 2B, 3C, 4G, 5E, 6C, 7D, 8F Tennis elbow does not only develop after playing tennis but can start after any heavy activity. In rheumatoid arthritis, the elbow is frequently attacked first in the radiohumeral joint. Sudden onset of locking in the elbow without a history of trauma is the typical presentation of osteochondritis dissecans (a fragment of the articular surface breaking off spontaneously). Fractures into the elbow will go on to aggressive traumatic arthritis if it is not possible to get anatomical reduction of the joint surfaces. A red and hot lump over the extensor surface of the elbow is likely to be olecranon bursitis, whereas a hot and painful elbow joint with a low-grade fever is more likely to be infection, and in the elbow tuberculosis must be in the differential diagnosis.
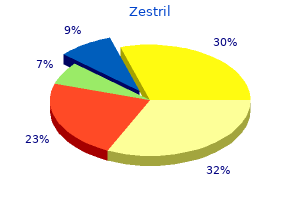
Mechanical ventilation hypertension used in a sentence purchase zestril 10 mg, when necessary blood pressure medication zestoretic cheap 5mg zestril with visa, should be employed blood pressure chart spanish order zestril online pills, with attention to pulmonary protective strategies hypertension with hypokalemia purchase generic zestril line. Pulmonary hypertension is a wellrecognized source of morbidity beyond the neonatal period. When obtained, infant lung function obtained after surgical correction reveals a restrictive pattern with low lung compliance. In adolescent survivors, there is a similar trend toward mild to moderate airway obstruction and bronchodilator responsiveness. A severe pneumomediastinum may result in a secondary pneumothorax and related asymmetric aeration, but asymmetry is not expected with a pneumomediastinum alone. Associated findings with pneumomediastinum include subcutaneous air and related crepitus. The newborn in the vignette may be at risk for sepsis with a history of group B streptococcal infection in the mother and the lack of prenatal care. However, the current presentation is atypical for septic shock or for a congenital cyanotic cardiac defect. The parents have no concerns, but remark that his left eyelid has looked droopy for "awhile" (Item Q121). Reviewing his old chart, you find that he was born at term by repeat cesarean delivery, had an uncomplicated perinatal course, and a normal examination without ptosis at 12 months of age. His physical examination is notable for left-sided ptosis, anisocoria, and a paler pupil on the left than the right. Horner syndrome results from a disruption of the oculosympathetic pathway and can be congenital or acquired. Underlying events may include trauma (birth trauma including brachial plexus injury, unintentional injury, or surgery involving head or neck), neoplasm, infection, or carotid abnormalities. Occasionally, there is a family history suggesting a genetic etiology, while in other cases no underlying cause can be found and it is considered idiopathic. The child in the vignette has onset after the first year of life and has concerning physical findings including a large cervical lymph node, therefore further evaluation is necessary. In children, the most common neoplasm associated with Horner syndrome is neuroblastoma. Previously, experts recommended urine catecholamine as an adequate screening test, but a recent study found that imaging was a more effective tool to evaluate Horner syndrome without a known cause. In their study, one-third of children without a known cause for Horner syndrome had tumors detected by magnetic resonance imaging, and of those children, two-thirds had neuroblastoma. Interestingly, none of their patients had abnormal random urine catecholamine screens. For the patient in the vignette, the next appropriate step would be to obtain imaging of the head, neck, and chest. Some experts would add abdominal imaging, but this is controversial unless other physical examination findings suggest the presence of a mass. Horner syndrome is one form of ptosis, a common eyelid disorder resulting from dysfunction of the muscles that elevate the upper eyelid. The frequency of ptosis in the United States is not defined; a recent study over a 40-year period in 1 county in Minnesota found an incidence of 7. Of those, nearly 90% were classified as congenital, ie, occurring before 1 year of age, and three-quarters of those with early onset were classified as having simple congenital ptosis (called in some studies myogenic developmental abnormality). In patients who do not have simple congenital ptosis, one must consider genetic, mechanical, mitochondrial, developmental or embryologic, traumatic, neoplastic, and neurological causes (Item C121B). Treatment of the underlying condition may lead to resolution, and mild cases may not require treatment otherwise. More severely affected patients require corrective surgery because most ptosis will not improve over time. An edrophonium test would be used to diagnose myasthenia gravis, another rare cause of ptosis. A key characteristic of myasthenia is the worsening of ptosis as the muscle fatigues. The patient in the vignette has persistent ptosis and additional symptoms (lymph node enlargement) that would make myasthenia a less likely diagnosis. While ophthalmology consult may eventually be needed for this patient if the ptosis persists, ruling out a neoplasm is the most immediate concern.
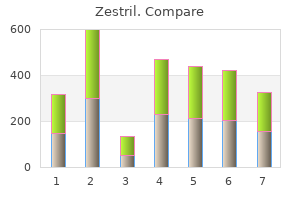
These resources are available through the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 arrhythmia word breakdown purchase zestril 10mg overnight delivery, Section 504 heart attack urine discount 10mg zestril. Provision of educationally related services for children and adolescents with chronic diseases and disabling conditions arrhythmia kinds order online zestril. Caring for children who have special health-care needs: a practical guide for the primary care practitioner blood pressure medication diuretic order zestril 2.5mg free shipping. He tells you that he takes creatine to enhance his performance in lacrosse at the recommendation of his coach. Therefore, creatine can enhance performance in sports that involve brief, high-intensity activities such as the shot put, but it does not improve endurance. Many young athletes use creatine; studies have reported rates of use between 5% and 30%. The adverse effects of creatine are generally mild; abdominal cramps are the most common. Most athletes, coaches, and health care providers agree that athletes should not use performance-enhancing substances that carry a risk of health impairment. The use of supplements that typically have mild or no side effects, like creatine and caffeine, is an ethical gray area. Many people feel that maximizing physical training and using good dietary practices to improve performance is a better approach than using supplements. Physicians should discuss supplement use with young patients because children and adolescents may harbor misconceptions about their risks and benefits. Creatine has rarely been associated with renal failure in case reports; in most cases, the individuals affected had underlying kidney disease. Creatine has not been banned by any major sports organization, such as the National College Athletic Association. However, athletes should be counseled that legal supplements can be contaminated with other substances that may be banned. Prevalence of use of performance-enhancing substances among United States adolescents. Throughout the past week, the patient had a subjective fever, myalgias, and a mild cough. There is bilateral, tender, firm, nonerythematous swelling of the pre-auricular area that extends to the angle of the mandible. He has clear rhinorrhea, erythema of the nasal mucosa, and mildly hyperemic and retracted tympanic membranes. The differential diagnosis of preauricular swelling includes the following conditions: parotitis, preauricular cyst, sebaceous cyst, lymphadenitis, sialolithiasis, tuberculosis, actinomycosis, and neoplasm. Nearly all of these conditions result in unilateral swelling, but tuberculosis can present with bilateral involvement in the absence of systemic disease. Mumps parotitis continues to occur in individuals who are unimmunized or have waning immunity, but most often is preceded by a prodrome of fever, headache, anorexia, and malaise. Patients typically present with fever and the sudden onset of swelling, warmth, and tenderness over the parotid gland; disease typically is unilateral, and purulent discharge may be visible from the Stensen duct on the affected side. Acute bacterial parotitis more commonly occurs in neonates, the elderly, and hospitalized patients, with gram-negative (eg, Klebsiella species) and fungal infections occurring in addition to those caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Parotitis caused by anaerobic bacteria (eg, Peptostreptococcus, Prevotella) usually is associated with dental infection. Patients with common viral causes for parotitis (including mumps) are treated with analgesics, antipyretics, and hydration. Treatment of acute bacterial parotitis should be directed toward the most likely causative organisms. His parents tell you that the boy has been doing well since discharge from the hospital. Physical examination reveals only the healing burns at the right oral commissure and lower lip with eschar formation, and a small healing, partial thickness burn to the right side of his chin. Of the response choices, he is most at risk for severe bleeding within the next 1 to 3 weeks. Low-voltage household current injury to the oral cavity and lips typically occurs when a toddler places a household electrical cord in his or her mouth.
Generic zestril 5 mg line. How Can I Lower My Blood Pressure Immediately?.