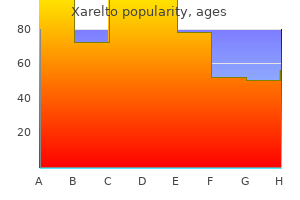
"Order xarelto on line amex, treatment variable".
By: I. Ashton, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, University of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine
Koskinas treatment juvenile rheumatoid arthritis cheap xarelto amex,2 Gesthimani Misirli medicine 0552 buy xarelto online from canada,1 Christos Vaklavas symptoms 14 days after iui discount 10mg xarelto,3 Apostolos Hatzitolios4 and George D treatment jaundice buy 2.5mg xarelto with amex. In the face of the established lipid lowering and the emerging pleiotropic properties of statins, the patient population suitable for long-term statin treatment is expected to further expand. An overall positive safety and tolerability profile of statins 172 Chatzizisis et al. Skeletal muscle-related events are the most common adverse events of statin treatment. Statin-induced myopathy can (rarely) manifest with severe and potentially fatal cases of rhabdomyolysis, thus rendering the identification of the underlying predisposing factors critical. The purpose of this review is to summarize the factors that increase the risk of statin-related myopathy. Data from published clinical trials, metaanalyses, postmarketing studies, spontaneous report systems and case reports for rare effects were reviewed. Briefly, the epidemiology, clinical spectrum and molecular mechanisms of statin-associated myopathy are discussed. We further analyse in detail the risk factors that precipitate or increase the likelihood of statin-related myopathy. Individual demographic features, genetic factors and co-morbidities that may account for the significant interindividual variability in the myopathic risk are presented. Physicochemical properties of statins have been implicated in the differential risk of currently marketed statins. Pharmacokinetic interactions with concomitant medications that interfere with statin metabolism and alter their systemic bioavailability are reviewed. Of particular clinical interest in cases of resistant dyslipidaemia is the interaction of statins with other classes of lipid-lowering agents; current data on the relative safety of available combinations are summarized. Finally, we provide an update of current guidelines for the prevention and management of statin myopathy. The identification of patients with an increased proclivity to statininduced myopathy could allow more cost-effective approaches of monitoring and screening, facilitate targeted prevention of potential complications, and further improve the already overwhelmingly positive benefit-risk ratio of statins. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is the most frequent cause of morbidity and mortality in developed countries. Statins confer a small but definite risk of myopathy, a dose-dependent adverse effect associated with all statins (class effect). The association of statins with cases of Drug Saf 2010; 33 (3) Statin-Induced Myopathy: Risk Factors and Drug Interactions 173 severe myopathic events may have resulted in excessive safety concerns for this revolutionary class of medications. The purpose of this review is to investigate the risk factors that precipitate statin-induced muscle adverse events, and also to summarize current guidelines on the administration of statins with regard to their potential myotoxicity. Rhabdomyolysis represents the least frequent, though potentially fatal, complication caused by skeletal muscle breakdown, which leads to the release of toxic intracellular constituents into the blood circulation and eventually causes acute renal failure. The lack of consensus in the definition of statin-induced muscle events hinders the precise Table I. Because patients with a considered high susceptibility to statin toxicity are generally excluded from clinical trials of statins, reported adverse event rates from controlled trials may underestimate the true rate of these adverse effects in an unselected patient population. Comparison between Statins Reports associating the use of all marketed statins with the entire spectrum of myopathy suggest that this is a class effect. On the basis of current evidence, and in the absence of randomized trials directly comparing the risk of each available statin in comparable doses and with standard definitions of myopathic events, no definite conclusions on the relative myopathic potential conferred by each of the currently marketed statins can be drawn. Mechanisms of Statin-Induced Myopathy the pathogenetic mechanisms of statin-induced myopathy have been thoroughly reviewed by Vaklavas et al. Reduction of prenylated proteins can result in dysprenylation of proteins, including lamins and small guanosine triphosphatases, thereby causing an imbalance in the intracellular signalling cascades and enhancing apoptosis. Sarcolemmal cholesterol deficiency, as a result of the dynamic equilibrium between membrane and plasma lipids, may adversely modify membrane physical properties, integrity and fluidity, thus resulting in membrane destabilization. Statin-mediated reduction of circulating, but not intramuscular,[31] CoQ10 levels has been reported, while no direct association between decreased intramuscular CoQ10 levels and mitochondrial myopathy has been established. Accordingly, CoQ10 deficiency may represent a predisposing rather than etiopathogenic factor of statin mediated myopathy, possibly in a synergistic manner with coexisting CoQ10-depleting conditions.
Under aerobic conditions cytochrome o or cytochrome aa3 serves as the terminal oxidase symptoms 28 weeks pregnant cheap xarelto 2.5mg amex. Under denitrifying conditions symptoms nicotine withdrawal discount xarelto 10 mg without prescription, quinol reduces nitrate reductase (NaR) medicine emoji buy xarelto toronto, and other reductases are reduced by cytochrome c medicine 7 year program cheap generic xarelto uk. In Paracoccus denitrificans, nitrate reductase and nitric oxide reductase are cytoplasmic membrane proteins while nitrite reductase is located in the periplasm. The [Fe-S] centres of the subunits participate in electron transfer within the molecule, and the b-type cytochromes of the subunit are involved in electron transfer from quinol to the [Fe-S] clusters (Figure 9. Springer, New York) Nitrate is reduced to nitrite by nitrate reductase (1) that oxidizes quinol. Two molecules of nitric oxide are reductively condensed to nitrous oxide by nitric oxide reductase (3). The b-type cytochrome associated with the subunit is reduced, oxidizing quinol and liberating protons. The [Fe-S] cluster of the subunit transfers electrons from the subunit to the subunit where nitrate is reduced to nitrite. The subunit takes electrons using b-type cytochromes from the reduced quinone and transfers them to the subunit through the subunit involving a [3Fe-3S] cluster and three [4Fe-4S] clusters. The nitrate reductase that initiates denitrification is different from the assimilatory nitrate reductase that is involved in the use of nitrate as a nitrogen source (Section 6. Energy in the form of the proton motive force is not conserved by the assimilatory enzyme. Two different nitrite reductases are known, one containing c-type and d-type cytochromes (cdNiR) and the other a copper protein (CuNiR). CuNiR is widely distributed in prokaryotes including Gram-positive denitrifiers such as species of the genus Bacillus, Gram-negative bacteria such as Pseudomonas aureofaciens and in archaea (species of the genus Haloarcula): cdNiR is found only in Gram-negative bacteria. Cytochrome c or a Cu-containing small protein, pseudoazurin, provides electrons to the homodimeric cdNiR. The gene for nitric oxide reductase has been identified and its mutant cannot grow under denitrifying conditions. Nitric oxide reductase is a complex enzyme consisting of a small subunit containing c-type cytochromes and two large subunits containing b-type cytochromes. Since less energy is conserved in denitrification than in aerobic respiration, denitrification is strongly inhibited by O2 with few exceptions. The expression of the genes for denitrification is regulated, and so are the enzyme activities after they are expressed. When the culture is transferred from anaerobic to aerobic conditions, the enzymes are slowly irreversibly inactivated. The enzymes become inactive under aerobic conditions because their affinity for reduced coenzyme Q and cytochrome c is lower than that for aerobic respiratory enzymes. Organisms utilizing more than one electron acceptor have elaborate regulatory mechanisms to conserve more energy under given growth conditions. Electron acceptors with a higher redox potential are preferentially used over those with a lower redox potential. Through these mechanisms, oxygen represses the expression of anaerobic respiratory enzymes. The expression of the nitrate reductase gene is further stimulated by a two-component system, NarX/NarL, in the presence of nitrate (Section 12. Another two-component system, NarQ/NarP, controls expression of the other enzymes of denitrification including nitrite reductase, nitric oxide reductase and nitrous oxide reductase. However, this process has now been identified in many other organisms including fungi such as Fusarium oxysporum and related strains, Cylindrocarpon tonkinense, Fusarium solani, Gibberella fujikuroi, Talaromyces flavus, Trichoderma hamatum and Trichosporon cutaneum.
The following sections will outline the major components of a typical culture medium for animal cells as well as their typical concentrations and their functions in cell metabolism symptoms your period is coming purchase xarelto 15mg online. Water One of the basic components of a culture medium medications54583 buy xarelto australia, and also one of the most critical symptoms of the flu discount xarelto 10mg visa, is water symptoms type 2 diabetes buy 2.5 mg xarelto. Culture media for animal cells 115 quality, since this can be the source of contamination that can affect cell growth. Potential contaminants include inorganic compounds (heavy metals, iron, calcium, and chloride), organic compounds (detergents), microbial-related contaminants (endotoxins and pyrogens), besides particles and colloids from several different origins. Since the presence of any of these contaminants can prevent cell culture on any scale, strict purity standards of water quality must be maintained. Efficient water purification systems are, therefore, required, and can be based on multiple-distillation systems or on equipment combining deionization, microfiltration, and reverse osmosis. The water used in the preparation of industrial culture media should be subjected to similar purification methods and should be continuously monitored to ensure the physicochemical and microbiological standards established by national pharmacopoeia. The standards for water employed for pharmaceutical use in different countries are described in Table 5. Lactate accumulation in the culture medium indicates that the citric acid cycle may not function in vitro similarly to the way it does in vivo. There is evidence that a significant amount of carbon may be assimilated from glutamine, and not from glucose, and that explains the large requirement for this amino acid by some cell types. Insect cells, in general, accumulate lactate at lower levels than mammalian cells. However, lactate can still be produced by these cells in media with low oxygen concentrations. The accumulation of lactate in high density cultures is a problem, since it causes medium acidification. Also, this compound is toxic to the cells, inhibiting cell growth when present in large concentrations. The substitution of part of the glucose by mannose, fructose, galactose, or maltose reduces glucose consumption rate and, as a consequence, also reduces the lactate formation rate. However, total substitution may affect protein glycosylation patterns, altering proteins such as antibodies. These include specific amino acids such as cysteine and tyrosine but the requirement varies between cell lines. Amino acids are necessary for protein, nucleotide, and lipid synthesis and, in addition, may be used as an energy source. These compounds can be provided as a defined mixture or in the form of protein hydrolysates, such as lactoalbumin, or plant-derived hydrolysates, like colza (Deparis et al. The concentrations of amino acids added to insect cell culture media are much higher than those found in media for vertebrate cells (Echalier, 1997), probably due to the fact that higher amino acid concentrations are found in insect hemolymph (insect body fluid) in comparison with blood serum. Glutamine, methionine, and serine are growth-limiting amino acids (Freshney, 1992). Glutamine acts as a source of carbon, nitrogen, and energy, and is normally added to the culture medium at high concentrations, varying from 1 to 5 mM. Special attention should be given to its stability, since glutamine spontaneously degrades by cyclization to pyrrolidone carboxylic acid in the culture medium. Glutamine is prone to thermal degradation (at 358C, for instance, glutamine is 50% degraded in only 9 days), and therefore, should be periodically replenished when required. The main metabolite generated from glutamine metabolism is ammonium which, similarly to lactate, presents toxic effects and is a cell growth inhibitor when accumulated in large quantities. It can be converted Culture media for animal cells 117 enzymatically to glutamic acid, leucine, and isoleucine by enzymes found in cells and also in the blood serum normally added to culture media (Freshney, 1992). Nevertheless, when serum-free media are employed, not only the water-soluble vitamins should be provided, but also the lipidsoluble ones, such as biotin, folic acid, niacin, panthotenic acid, thiamine, and ascorbic acid, as well as the vitamins B12, A, D, E, and K. Vitamins are used in very low amounts as enzyme cofactors, essential for general cell metabolism. While ascorbic acid acts in collagen synthesis, vitamin A affects cell growth and differentiation. Vitamin E is an antioxidant agent, whereas vitamin D regulates calcium ion transport and acts as a hormone, being toxic when supplied in excess. Besides serum, yeast extract can also be used as an effective vitamin supply to culture media.
Posttraumatic stress disorder in rape victims: autonomic habituation to auditory stimuli treatment conjunctivitis xarelto 2.5mg online. Neurocircuitry models of posttraumatic stress disorder and extinction: human neuroimaging research-past symptoms thyroid cheap xarelto online amex, present treatment 8 cm ovarian cyst order xarelto with visa, and future symptoms questions cheap xarelto 20mg fast delivery. Evidence for hippocampal regulation of neuroendocrine neurons of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. The role of the hippocampus in feedback regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Inhibition of glucocorticoid secretion by the hippocampal formation in the primate. Neurocircuitry of stress: central control of the hypothalamopituitary-adrenocortical axis. Conflict between current knowledge about posttraumatic stress disorder and its original conceptual basis. Post-traumatic stress disorder in somatic disease: lessons from critically ill patients. Reorganization of the morphology of hippocampal neurites and synapses after stress-induced damage correlates with behavioral improvement. Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of dendritic remodeling in hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons. The role of the medial prefrontal cortex (cingulate gyrus) in the regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress. Regional differentiation of the medial prefrontal cortex in regulating adaptive responses to acute emotional stress. Dendritic reorganization in pyramidal neurons in medial prefrontal cortex after chronic corticosterone administration. Chronic behavioral stress induces apical dendritic reorganization in pyramidal neurons of the medial prefrontal cortex. Stress-induced alterations in prefrontal cortical dendritic morphology predict selective impairments in perceptual attentional setshifting. Consolidation of fear extinction requires protein synthesis in the medial prefrontal cortex. Morphological correlates of corticosteroid-induced changes in prefrontal cortex-dependent behaviors. Specific configuration of dendritic degeneration in pyramidal neurons of the medial prefrontal cortex induced by differing corticosteroid regimens. Induction and habituation of immediate early gene expression in rat brain by acute and repeated restraint stress. Chronic stress impairs rat spatial memory on the Y maze, and this effect is blocked by tianeptine pretreatment. Pre- and posttraining infusion of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists into the amygdala impair memory in an inhibitory avoidance task. Neurons of the lateral and basolateral amygdaloid nuclei: a Golgi study in the rat. Recovery after chronic stress fails to reverse amygdaloid neuronal hypertrophy and enhanced anxiety-like behavior. Stress duration modulates the spatiotemporal patterns of spine formation in the basolateral amygdala. Prolonged behavioral stress enhances synaptic connectivity in the basolateral amygdala. Adaptive and maladaptive psychobiological responses to severe psychological stress: implications for the discovery of novel pharmacotherapy. Neural plasticity, neuropeptides and anxiety in animals-implications for understanding and treating affective disorder following traumatic stress in humans. Glucocorticoid receptor activation is involved in producing abnormal phenotypes of single-prolonged stress rats: a putative post-traumatic stress disorder model. Transgenic brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression causes both anxiogenic and antidepressant effects.
Generic xarelto 2.5mg without a prescription. Seinfeld: Kramer - Gonorrhea!.