"Purchase mefenamic 500 mg, spasms causes".
By: Y. Miguel, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Creighton University School of Medicine
Dilbert Dunker and Helicopter Escape Trainer the Dilbert Dunker consists of a simulated aircraft cockpit section mounted on rails which extend into a swimming pool muscle relaxant and tylenol 3 generic mefenamic 250 mg visa. The trainee spasms caused by anxiety order mefenamic 250 mg with visa, after receiving proper indoctrination spasms rectal area generic mefenamic 250 mg on-line, is seated in the cockpit with shoulder harness and lap belt secured infantile spasms 2013 buy generic mefenamic online. The cockpit assembly is released and slides into the water, and the forward section (nose) is rotated down until the cockpit is inverted and completely immersed. After all motion stops, the trainee releases the restraints, exists the cockpit, and surfaces. As a safety precaution, specially trained scuba-equipped swimmers are located in close proximity to observe the actions of the trainee and lend assistance if necessary. A number of these devices have been distributed to various Navy and Marine Corps activities. Parachute Harness Release Training Two devices are used to demonstrate problems associated with parachute harness release. One device, the Para-Drag, allows students to experience problems in releasing parachute harness fittings under conditions simulating those which would be found when an aviator is dragged across the surface of the water by the parachute canopy. With this device, the student can experience problems with shroud line entanglement, and become acquainted with the difficulties involved in locating and operating the seat pan release mechanism during parachute descent. Helicopter Hoist In this exercise, each type of hoisting apparatus currently in operational use is placed in the water where the trainee demonstrates the ability to board or enter each device properly and is then hoisted vertically just clear of the water. Arrangements are made with a helicopter squadron or unit to perform actual hoists from an offshore location or from a nearby bay or lake. This permits indoctrination in boarding both the rescue device and the rescue craft while in the actual downwash created by the helicopter rotor blades. Ejection Seat Training In addition to the above, aircrew members of ejection seat equipped aircraft receive training in the proper procedures for use of the ejection seat in their aircraft. Training is centered on the aeromedical aspects of ejection rather than when to eject, or how the system works. These are static devices which duplicate the specific seat installed in a particular aircraft and, in some cases, a portion of the cockpit itself. The procedure trainer provides indoctrination in the sequence of activities necessary for successful ejection: body position, actuation sequence, secondary methods of actuation, etc. While afloat or when stationed at a place which does not have a procedure trainer, a deactivated ejection seat may be used as a training device. All cartridges, both propulsion and gas initiator, must be removed and should be actually sighted by personnel prior to sitting in the seat or actuating seat controls. This is best accomplished during required periodic inspection of the aircraft and seat, when it will not interfere with aircraft utilization, or by using seats that have been recovered from a mishap and have been checked and verified to be safe. The Universal Ejection Seat Trainer Device 9E6 utilizes a choice of ejection seats, a pneumatic charge, and a set of rails which project upward and backward at an angle of 18 degrees from the vertical. Prior to ejection, the height and weight of the aviator are taken, the seat is adjusted for that height, and the pneumatic charge setting is adjusted for that specific weight. The aircrew member assumes the recommended body position, Upon actuation of the face curtain, or lower ejection handle the pneumatic charge propels the seat and occupant up the guide rails approximately 6 to 7 feet. This type of training has proved to be extremely effective, if closely monitored and used to enforce and reinforce correct usage and operation of the system. Aircrew members who have made emergency ejections indicate that the dynamic training prepared them for the actual emergency condition and aided in relieving apprehension concerning catapult firing. The vast majority of these training devices are available at the Aviation Physiology Training Units scattered throughout the fleet. For more information concerning aviation escape and survival training, consult a U. Future Escape and Survival Systems Ejection Seats the performance characteristics and reliability of existing seats are continually being updated to match the increased performance of new aircraft. Work is proceeding toward the development of a seat mounted electronic sequencer and controller which will eliminate the two, three and four mode sequencing systems presently being used to control ejection events. The heart of this new system is a microprocessor which expands timing selectivity and decision making capabilities to optimize seat performance under all ejection circumstances.
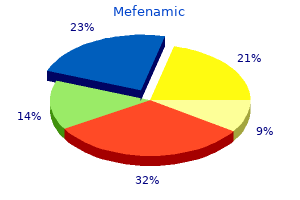
Conclusion: this study has found a high prevalence of uncorrected refractive errors among the internally displaced children in Iraq muscle relaxer z order cheapest mefenamic. This result represents an important health issue among those children spasms homeopathy buy cheap mefenamic line, requiring major actions to tackle and resolve it spasms leg order discount mefenamic on-line. Key-words: Internally displaced children spasms with spinal cord injury purchase mefenamic 250mg free shipping, Cross-sectional study, Refractive errors, Prevalence, Iraq. Therefore, the need for an effective screening programs to detect Corresponding author: Dr Rafea Allawi Fayyadh College of Medicine / University of Fallujah, Iraq E-mail: dr. One of its strategies is to include a simple visual acuity test into the school health programs, and to perform spectacles provision to children with significant refractive errors [4, 5]. Provision of appropriate spectacles is considered as a simple, costeffective strategy in order to improve vision. In Iraq, as a result of the violence and conflicts in the past decade, more than 1. To our best knowledge, there is no available published data or information regarding the prevalence of visual impairment among these internally displaced children. Therefore, this study aimed to draw attention to the on-going health problems of the internally displaced people by determining the prevalence of the uncorrected refractive errors among the displaced schoolchildren. The students were recruited from 8 primary schools for internally displaced children located in Kurdistan region, North Iraq. The study included all the cooperative students of both genders from these schools after obtaining informed consents from their parents or guardians. The age of students included in the study ranged from 6 to12 years; since in Iraq, children enroll in the elementary schools at age of 6 years, and the duration of study is six years. Ophthalmic Examination All the medical procedures were performed by trained ophthalmologists and optometrists. Children already wearing spectacles at time of examination were also examined and any changes in refractive errors were noted. The visual acuity, types of refractive error and correction were noted down in a self-designed proforma. Astigmatism was further classified into: simple myopic, simple hyperopic, compound myopic, compound hyperopic and mixed astigmatism. Results Study population A total of 592 students from 8 primary schools for internally displaced children in Kurdistan region, Iraq, were recruited for this study. We excluded 8 cases from the data analysis because of poor cooperation and missed information. The results of the vision screening according to gender and age of the participants are shown in Tables 1 and 2. Table 1: Overall results of vision screening in schools of internally displaced students in Iraq by gender. Age group (years) 6 -7 7 -8 8 -9 9 -10 10 11 11 - 12 Total Visual acuity 6/9 or better Number (%) 161 (29. Causes Refractive error Amblyopia Keratoconus Retinal disease Total Number (%) of students with visual impairment 178 (32. Tables 4 and 5 are showing the prevalence of refractive error types distribution according to gender and age of the examined schoolchildren. Results of refractive errors prevalence studies throughout the worlds vary widely. In Iraq, the prevalence of refractive errors among schoolchildren has been studied in a limited number of studies; in Amara city was (47%) [7], in Thiqar governorate was (35%) [8], in Erbil governorate was (25%) [9], and in Massif Kurdistan was (23. In other studies around the world, refractive errors prevalence among children were; (26. This wide variation in the results could be explained by; the racial and genetic factors of the different countries [18], the difference in the sampling methods and by the sample size. While in our study it was (6 - 12) years, other studies had older or younger age groups included. This can be explained by the fact that; as a result of the conflicts in their cities, many of these children never had a previous visual examination. Also, for those who had previously examined and prescribed spectacles, the low Medico-legal Update, January-March 2020, Vol.
Order mefenamic 250 mg overnight delivery. 20151117 Neuromuscular Blocking Agents Basic Pharmacology.
Syndromes
- Drinking a lot of alcohol
- Has difficulty seeing
- Stiff neck
- Blood work, possibly including arterial blood gases
- Feeling ill
- When did you first notice blood in your urine? Has the amount of your urine increased or decreased?
- Signs of niacin-deficiency disease (pellagra)
- Coma
- Carbonated drinks