"Order cheap xtane, chi infra treatment".
By: V. Mezir, M.A.S., M.D.
Clinical Director, Morehouse School of Medicine
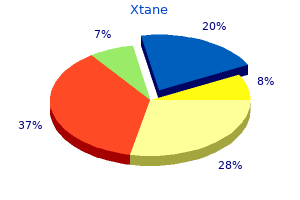
Ecosystems affected by land degradation (including medicine dispenser buy xtane overnight delivery, for example medicine xanax generic xtane 25 mg on line, some areas that have been transformed to agricultural systems and urban areas) mainly include forests treatment hyperthyroidism purchase 25mg xtane with amex, rangelands and wetlands medicine lake montana safe 25mg xtane. Wetlands are particularly degraded, with 87 per cent lost globally in the last 300 years, and 54 per cent since 1900 {4. Land degradation, including transformation to urban areas and to intensive agricultural systems 8. The extent of transformation in developed countries is large, even though the rate of transformation has slowed or even reversed in recent decades. In developing countries, the extent of transformation is lower, but the rate of transformation remains high. In the future, most degradation and especially transformation is forecasted to occur in Central and South America, sub-Saharan Africa and Asia, which have the largest remaining amount of land suitable for agriculture (well established). This figure shows the trade-offs among ecosystem services and biodiversity with land use intensification, using food production as an example. In this specific example, as food production increases, there is a decrease in other ecosystem services and biodiversity (illustrated by reduced bars) as compared to the undegraded state. In extreme cases, land has been degraded to the point of abandonment (right panel), thus providing less of all ecosystems services. Deciding whether trade-offs among land-use types are negative or beneficial depends on values and priorities, and is therefore part of the socio-political decision-making process. Evidence suggests there are few, if any, beneficiaries from extreme degradation and the permanent loss of function and services. Between 1970 and 2012, the index of the average population size of wild terrestrial vertebrate species declined by 38 per cent and that of freshwater vertebrate species by 81 per cent (established but incomplete) {4. Species extinction rates are currently hundreds to thousands of times above the long-term rate of species turnover (established but incomplete) {4. There is a body of evidence suggesting a positive association between diversity, especially functional biodiversity, ecosystem functions and resilience to disturbance (established but incomplete) {4. Land degradation has already had a pronounced impact on ecosystem functions worldwide (well established). Net primary productivity of ecosystem biomass and of agriculture is presently lower than it would have been under natural state on 23 per cent of the global terrestrial area, amounting to a 5 per cent reduction in total global net primary productivity (established but incomplete) {4. Over the past two centuries, soil organic carbon, an indicator of soil health, has seen an estimated 8 per cent loss globally (176 gigatons of carbon (Gt C)) from land conversion and unsustainable land management practices (established but incomplete) {4. Projections to 2050 predict further losses of 36 Gt C from soils, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa {7. These future losses are projected to come from the expansion of agricultural land into natural areas (16 Gt C), degradation due to inappropriate land management (11 Gt C) and the draining and burning of peatlands (9 Gt C) and melting of permafrost (established but incomplete) {4. Indigenous and local knowledge includes practices and beliefs about relationships of living beings, including humans, with one another and their environment. This knowledge evolves continuously through interaction of experiences and different types of knowledge, and can provide information, methods, theory and practice for sustainable management that has been tested through application and experimentation in real-world situations, by many people, over a wide range of conditions. This report is based on expert opinions from 28 authors working on the assessment with a wide range of land degradation and regional experience. Three or more experts contributed to each cell unless denoted by an asterisk (*), which indicates two expert opinions. Data was not reported when fewer than two experts contributed to the scoring, which is denoted by the grey cells. Within each region, the impacts on biodiversity and ecosystem services in managed systems. The five land degradation drivers of non-timber natural resource extraction, extractive industry and energy development, infrastructure, industry, and urbanization, fire regime change and introduction of invasive species were evaluated relative to the inferred state of biodiversity and ecosystem services in the absence of human disturbance (Box 1. In the analysis, however, the scores of biodiversity and ecosystem services were highly correlated (range = 0. Consequently, changes in biodiversity and ecosystem services are reported as one integrated score. Trends in land degradation from 2005 to 2015 due to specific drivers are shown by the angle of the arrows. Within the agricultural production drivers, the extent of land affected by the degradation driver is expressed as a percentage of the total land area of that land use type. The extent of land affected by the degradation driver of the remaining five drivers is expressed as the total land area of the subregion.
One solution treatment hiatal hernia order 25 mg xtane free shipping, if no authorisation to clear is obtained medicine 911 generic xtane 25 mg on line, is to buy existing neighbouring lands to enlarge the farming area symptoms zinc deficiency husky buy discount xtane 25mg. Unlike in the far area (west of Tsinjoarivo) treatment 2011 buy xtane canada, many children do not attend school and there is no access to medical care. A village chief in the intermediate area explained that shifting cultivation is not practiced in the forest. The rice plantations existed before the bans and they are not extended by their owners; however they cut the wood surrounding the plots to improve exposure to the sun. In the past, farmers from the forest fringe supplied agricultural products to inhabitants of the far area. Now, the opposite occurs because of the dif culties of obtaining permits to clear forest areas. The land used to be fertile, but now yields are decreasing and farmers lack money to buy chemical fertilizers. Conservation projects grant access to water to compensate villager groups for their efforts to manage their forests around the national park in a sustainable manner. In this area, about 75% of the interviewed farmers consider their subsistence as dependent on the forest. However, there is a signi cant difference among the farmers of Tsinjoarivo, depending on their location. Interviewed farmers living far from the forest stated that their subsistence does not depend on the forest. However, even the use of the term forest is ambiguous because some consider small planted patched of Pinus and Eucalyptus as "the forest. Construction and fuelwood come from private eucalyptus and pine plantations that also help to prevent erosion. Instead, they extracted wood resources directly from the forest and did not need to manage a plantation. In Manompana and Tsimanampetsotsa, farmers did not plant trees for fuelwood - they either collected it around the village or had to buy it. This can be explained by the opportunities available to sell products during two weekly markets and by road connections to the nearest city and the capital of Antananarivo, enabling distribution of the products. In Tsimanampetsotsa, the dryness of the region regularly leads to periods of starvation and prevents cultivation of as many vegetables and fruit trees as in Tsinjoarivo (ve +/-two products versus ten +/-two products per farmer). Labour is generally provided by the family - only 8% of respondents paid for additional labour (compared to 21% in Tsinjoarivo and 28% in Manompana) to maximize their annual yields. The percentage of income from selling tavy products (rice in Manompana and maize or cassava in Tsimanampetsotsa) compared to the farm income (red bars) and the share of the total value of products from tavy (green bars) for each quartile is calculated. It shows that incomes of the poorest households are most dependent on tavy: their income from tavy products represents 63% of farm incomes (red bars), against 21% for the richest households. In addition, the gure indicates that the richest households bene t more from tavy than the poorer households as they are able to turn a large part of the tavy products that they cultivate into income. This income represents 45% (green bars) of the total value of the tavy products in Manompana and Tsimanampetsotsa (against 2% for the poorest households). Dimension 1 separates high farm income, far area, and intermediate area on one side of the axis, with zero farm incomes and at the forest fringe on the other side. The gure illustrates that farmers at the forest fringe get less bene t from their agricultural activities. The study highlights that cultural, social, economic, and environmental factors interact and guide the behaviour of the actors. Alongside these, the subordination of technique and economy to social structures and the saturation of space need to be considered. The former describes traditional aspects of the Malagasy society, which may play a role in the poverty of Malagasy households. In Manompana, tavy is a traditional practice with religious elements and is still practiced even though its productivity is low.
Many countries are tempted to require that certain types of hardware or software integral to the operation of the network be physically sited within their national boundaries symptoms sleep apnea purchase 25mg xtane with amex. Reasonable liability rules regarding third-party activity Unbounded liability rules constitute a major barrier to international Internet commerce and communications medicines order 25mg xtane overnight delivery. Due to the extraordinary quantity of data transiting communications networks symptoms yeast infection men buy cheap xtane 25mg online, these businesses could be extremely vulnerable to strict 169 8 liability for the misdeeds of users medicine 1975 cheap xtane online mastercard. Congress responded to this problem in 1996 with Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act, providing categorical immunity from liability for user misconduct, thus allowing Internet companies to combat undesirable or potentially illegal activity without fear of additional liability for editing user content. Section 230 states that "no provider or user of an interactive computer service shall be treated as the publisher of any information provided by another information content provider. Unfortunately, the same robust protections for intermediaries are not universal and this has directly hampered U. In order to maintain the same robust pace of growth and innovation, national and international trade law must reflect the same principles that fostered growth in the U. The balance should provide proper protection for strategically important and constitutionally-rooted principles like fair use. Business certainty is needed for industries that may not 170 9 provide content but are nevertheless heavily regulated by copyright law. Statutory damages are a significant and measurable deterrent to innovation; these chilling effects could be mitigated by reforming disproportionate statutory damages to provide greater predictability and re-examining whether statutory awards should be permitted to aggregate infinitely. Copyright compliance has a great impact on early-stage investment, and, consequently, innovation as well as the economy. Interviews with hundreds of angel investors and venture capitalists found them to be overwhelmingly wary of new regulations and desiring an unambiguous copyright regime. In particular, increasing user or website liability would negatively affect innovation by driving early investors into other areas. A recent study found that such risks could have the effect of reducing the pool of interested angel investors by 81%, and that increased exposure for users would likely reduce the pool of interested angel investors by 48%. In general, 80% of investors polled reported being uncomfortable investing in business models in which the regulatory framework is ambiguous. Internet Copyright Regulations on Early-Stage Investment: A Quantitative Study (Booz & Company 2011), available at. See Josh Lerner, the Impact of Copyright Policy Changes on Venture Capital Investment in Cloud Computing Companies (Analysis Group 2011), available at 171 10. For example, in an industry or field where developments are made incrementally with lots of small improvements, patents are problematic because a single patent on a small improvement can block anything that tries to build on that improvement. The tech industry (especially software) is a classic example of this type of field. The current patent system is a better fit for industries where each product stands on its own, like pharmaceutical. Innovation report concludes by calling for improvement in three areas: clearer patents with a high standard of novelty and non-obviousness, reduced disparity of litigation costs between patent owners and technology users, and greater adaptability of the innovation system to challenges posed by new technologies and new business models. While the White House and the House of Representatives have made some progress in addressing reform, more needs to be done. Beyond the reforms supported by the President and the House of Representatives, we suggest: 1. Integrate patents and other means of appropriating returns into a coherent innovation policy grounded in realistic assessment of costs, risks, and benefits. Address the persistent quality problem by elevating the standard of obviousness from "person having ordinary skill" to peer review ("recognized skill"), and independently monitor allowance rates and evaluate causes (and consequences) of change. Monitor and assess real benefits and costs of the patent system; require reporting of assignments, licenses, settlements, contractual demands for indemnification, 172 11 and costs associated with global coverage and litigation; and require timely registration of assignments, licenses, notice/demand letters, litigation, and settlements. Confirm that economic outcomes should be the goal of the patent system, and that any discrimination should be measured in terms of outcomes. Provide expanded licensing guidelines for government-owned and governmentfunded inventions (prizes, grants, cooperative agreements, or contracts) to reflect economic considerations, including the contribution of public funding, the difference between combinatorial and discrete-product innovations, and the appropriateness of alternative means of achieving returns from innovation. Limit university participation in speculative/secondary markets by requiring meaningful steps toward commercialization within five years and requiring full reporting of licensing revenues. Broaden the Patent Public Advisory Commission beyond "user" and practitioner communities too predisposed to expanding the volume and scope of the system, and include economists and technology experts capable of evaluating the functioning and effectiveness of the system. Redesign the fee structure to eliminate the front-end subsidy (and internal incentive to allow marginal patents) except for small and micro entities as provided by Congress. Require owners of invalidated patents to reimburse fees paid by successful challengers (but allow patent owners an opportunity to abandon patents prior to administrative proceedings upon presentation of prior art or other invalidating evidence).

It has also helped promote the transition from forest exploitation to multiple-objective forest management and increased access to international markets treatment 7th feb cardiff buy xtane online from canada. However facial treatment discount 25 mg xtane mastercard, certi cation is not the correct instrument to address sector-wide problems medicine rheumatoid arthritis order xtane 25 mg with visa. Forests are important to very important to livelihoods in all of the analysed communities 3 medications that cannot be crushed purchase 25 mg xtane with mastercard. Job creation, better salaries, and investments in community infrastructure and services appear to be the main direct bene ts from forest management. The following conditions are reported to underlie positive trends in the case study areas: Reforms in the policy and regulatory framework are instrumental in creating the conditions for clarifying and recognising land-tenure rights in traditional community territories. This, in turn, paves the way for communities to engage in the community-forest management process. Local decisions regarding the protection of forests and drawing of rules and control measures for forestry activities are important for empowering communities and strengthening their capacities in negotiation and con ict resolution. Cultural identity and tradition play an important role in facilitating the internal organisation for decisionmaking and compliance. The development of local capacities for forest management, in some cases also including enterprise development, is fundamental to the process. The forging of alliances and partnerships with governmental and non-governmental organisations is instrumental in advancing community efforts for achieving their forest management objectives. Management strengths are linked to the diversi cation of forest uses through technological innovation and research to add value to forest products and services. The access to nancial resources for communitybased forest management is still quite dif cult, but some innovative ways of nancing forestry activities for smallholders are reported. Mainly as the result of efforts by external agencies, monitoring as a management tool has gained acceptance and interest. The usual entry point consists of monitoring the impacts of commercial timber operations through post-harvest evaluations. This is further aggravated by lack of policy implementation, weak law enforcement, and illegalities. However, the regulatory framework and policies discourage timber harvesting and trade and prevent communities from fully bene tting from opportunities generated by improved forest conditions. Similarly, in Uganda [22], efforts to encourage community forest management have been undermined by restrictions on the harvesting and commercialisation of timber and charcoal. This has been partially offset by an increase in the establishment of trees outside forests in plantations and agroforestry systems because an increase in prices for timber, charcoal, and poles has made tree-planting attractive. An intense forest con ict resulted in a dramatic shift in forest policy in all federal forestlands from sustainable yield forestry towards increased multi-stakeholder participation, ecosystem- and landscape-focused management, and re management. Science-based information and intensive planning exercises had an important role in the process. Isolated forestdependent communities show growing poverty and limited economic opportunity. Many have sought to develop business capacity to undertake restoration and manufacturing of value-added wood products, but in many communities, this has not replaced the losses brought on by the transformation of the timber industry. At the same time, international forest governance has developed into a complex, fragmented regime (Rayner et al. In addition to timber, ecosystem services that forests provide, and indigenous and community forest rights have gained prominence on the international agenda (Arts et al. This section focuses on the in uences of international processes and the related discourses on national and local policies and behaviour as reported in the case studies. In these cases, the rural population is still strongly dependent on forests but the rights to forests are insecure. In Madagascar, customary tenure system still prevails in some areas, but it is largely ignored by the state, which is the legal owner of all forests. Bernstein and Cashore (2012) distinguish between 1) international rules, 2) international norms and discourse, 3) interventions in markets, and 4) direct access to domestic policy-making processes.
What these models have in common is that they all rely on robust intellectual property to enable their success symptoms jock itch xtane 25 mg line. For example medicine 3605 xtane 25 mg visa, the popularity of open innovation relies on the use of open source licenses that permit reproduction medications bad for your liver generic xtane 25mg with amex, distribution medicine over the counter purchase discount xtane on line, and adaptation, but only on certain conditions (including the further availability of the work). Copyright law enables these terms and conditions and renders open source licenses enforceable. There are a number of factors, such as the specific technologies involved and market needs that influence how a business will choose to sell their goods and services. To stay competitive, we need to maintain a business-model independent intellectual property system. For example, critics of the availability of patents for software ignore the fact that today, software innovation is an indispensable aspect of advances in every field of technology and every sector of the economy. Patent protection provides a critical incentive for innovators to pursue new inventions and proceed to market, and this incentive should be recognized and preserved. Moreover, the need for proprietary-based innovation is often a reflection of the ease with which free riders may compete directly with the innovator. Common examples of this are commercial7 copyrightable software, movies, and music, which can be reproduced and distributed at virtually no cost in the modern marketplace. Similarly, products utilizing patented art that are vulnerable to reverse engineering are poor candidates for non-proprietary innovation. And to the extent that almost any successful product and company is subject to the fraud of counterfeiting, they must and do rely on trademark law to address such unfair competition. Innovators rely on both registered assets, as well as less formal rights like trade secrets. Trade secrets typically involve products, or more often services, that are difficult to replicate, such as a computer algorithm that drives a service. To be sure, there are many examples of open source software and user-generated content. But the overwhelming majority of innovation in these fields has been generated by commercial entities that employ large numbers of people and require a proprietary model to operate successfully. To the extent that intellectual property protection is weakened and/or enforcement is ineffective, innovators whose work might have been a better fit elsewhere will be forced to shoehorn their business into a trade secret model. Thus, open source advocates who seek to reduce intellectual property protection not only would undermine the framework of their own innovation model (and innovation, generally), they would drive others to be less open. Of course, trade secrets do play an important role in supporting American innovation for companies that choose that route. Strong trade secret protection is critical to enabling the collaboration that accelerates technology development and enables market access. Investing in innovation is not cheap and when innovators sense their hard-earned achievements are at risk, they will naturally limit what they share externally. The only protection available for this type of knowledge is self-help or trade secrets. And with trade secrets being one of the most underdeveloped areas of intellectual property law globally, many innovators may choose not to engage in critical opportunities that could improve U. In February, 2013, the Administration issued its "Strategy on Mitigating the Theft of U. Congress is currently considering a federal civil trade secret bill that could vastly improve the landscape for American innovators. The proposed legislation would empower them to take action against theft of their confidential information, by both preventing devastating losses and providing a path to recovery when they do occur. This lack of protection for innovation can prevent full engagement in the global market, which translates into fewer export-driven American jobs. Data Protection for Biologics In the 2011 Strategy, the Administration identified among its highest priorities to "accelerate biotechnology, nanotechnology, and advanced manufacturing. Unfortunately, rather than pursue this clear win, the Administration has repeatedly proposed reducing the needed protection in U.
Buy xtane 25mg on-line. Living with multiple sclerosis: Felix's story.