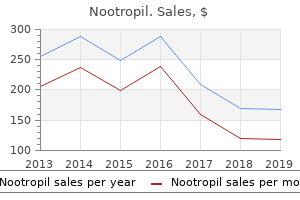
"Discount 800 mg nootropil with mastercard, medicine 4211 v".
By: E. Abe, M.B.A., M.D.
Professor, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
In laboratory culture they are found to be intolerant of the antibiotics or growth metabolites of other fungi symptoms whiplash buy generic nootropil, and they do not themselves produce antibiotics 247 medications buy nootropil. So symptoms 4 weeks discount 800mg nootropil with mastercard, these pioneer fungi typically have a short exploitative phase and a high competitive ability treatment of criminals buy nootropil with a visa. The sapstain fungi that rapidly colonize newly felled trees are typical pioneer saprotrophs. They grow in the nonwoody (parenchymatous) medullary rays and they discolor the wood by their darkly pigmented hyphae. Although they cause no structural damage to the timber, they can seriously reduce its marketable value. These staining fungi include several species of Ophiostoma (related to Ophiostoma ulmi which causes Dutch elm disease; Chapter 10). However, similar "bluestain" fungi such as Chlorosplenium aeruginascens (Ascomycota) cause an attractive turquoise pigmentation of wood. This used to be highly valued for producing inlaid veneers in decorative objects, termed Tunbridge Ware because the industry was based in the Kentish town of Tunbridge Wells. Polymer-degrading fungi Several fungi have an extended phase of growth on the major structural polymers such as cellulose, hemicelluloses, or chitin. Once established, these fungi tend to defend the resource against potential invaders, either by sequestering a critically limiting nutrient such as nitrogen or by producing inhibitory metabolites (Chapter 6). The large number of fungi in this category differ in the types of substrate they utilize, their different environmental requirements, and their growth in different phases of a decomposition sequence. When cereal straw and other cellulose-rich materials are buried in soil they are colonized by fungi such as Fusarium, Chaetomium, Stachybotrys, Humicola, or Trichoderma spp. A spectrum of salt-tolerant cellulolytic fungi is found on plant remains in estuarine waters. Chitinous materials are colonized by yet another group of fungi, such as Mortierella spp. Polymer-degrading fungi can exploit different microhabitats, and thereby coexist in a single substrate resource. Evidence for this has come from microscopical examination of transparent cellulose film ("Cellophane") buried in soil (Tribe 1960). These degrade the cellulose locally by forming finely branched rhizoids between the layers of the film. Other parts of the film can be colonized by mycelial fungi such as Humicola grisea, Fusarium spp. The Rhizoctonia and Fusarium colonies form loose networks over the surface of the film, whereas Humicola is seen as localized, compact colonies that "root" into the film and produce fans of hyphae within it, like the fans of Pythium graminicola shown in. Fungi that degrade recalcitrant (resistant) polymers Fungi that degrade the more resistant polymers such as lignocellulose (cellulose complexed with lignin) often predominate in the later stages of decomposition. Several of them are Basidiomycota, including Mycena galopus, a common small toadstool in the leaf litter of woodlands. Other common examples are the fairy ring fungi, frequently seen in old grasslands. These fungi grow on the thick mat of accumulated dead leaf sheaths of grasslands and spread progressively outwards year by year. Several fungi produce these rings, including the common edible field mushroom (Agaricus campestris). They usually cause no damage because they grow on dead organic matter, and often the only sign of their presence is a ring of more vigorous, lush growth of the grass, resulting from mineral nutrients released from breakdown of the organic matter. But the "fairy ring champignon" Marasmius oreades is an interesting exception because it can kill the grass. The reason is that this fungus produces a mass of fungal hyphae just beneath the grass surface, and these hyphae dry in mid summer, becoming hydrophobic and preventing water from penetrating the soil. Even fungicides are ineffective in preventing death of the grass, but surfactants (including dilute washing-up liquids) can reduce much of this damage. They might occur earlier, but they become conspicuous only after an initial phase of exploitation by Zygomycota and Penicillium spp. The ecological success of fungi that develop later in the decomposition sequence is related to their specialized ability to degrade polymers that most other fungi cannot utilize. However, it does not necessarily follow that they use these complex polymers as their main energy source.
The factors that control the development of mycelial cords are poorly understood medicine 123 order nootropil with american express, but studies on S medicine man 1992 buy discount nootropil 800 mg on-line. The wide medicine 627 discount nootropil 800mg mastercard, central vessel hyphae (vh) are surrounded by narrower sheathing hyphae (sh) symptoms 6dpiui buy nootropil in india. The surface of the mycelial cord is covered with extracellular matrix materials, and hyphae. Some hyphae (labeled d and also near the top right) have been sectioned through dolipore septa. Also, cords growing from a mineral nutrient medium onto an organic nitrogen medium gave rise to normal, diverging hyphal branches. Regulatory control by nitrogen seems logical for wood-decay fungi, because wood has a very low nitrogen content and these fungi could have evolved special mechanisms for conserving and remobilizing their organic nitrogen (Chapter 11). This could apply also to the cords of ectomycorrhizal fungi, because these fungi have a significant role in degrading organic nitrogen in otherwise nitrogen-limiting soils (Chapter 13). In terms of function, mycelial cords have been shown to translocate carbohydrates, organic nitrogen, and water over considerable distances between sources and sinks of these materials. The vessel hyphae seem to act like xylem vessels of plants, transporting water by osmotically driven mass flow (Chapter 7). The combination of their thick walls, the extensive extrahyphal matrix and reinforcement by fiber hyphae could enable vessel hyphae to withstand considerable hydrostatic pressure. Rhizomorphs Rhizomorphs serve similar functions to mycelial cords but have a more clearly defined organization. A notable example is the rhizomorph of Armillaria mellea, a major root-rot pathogen of broad-leaved trees. It spreads from tree to tree by growing as rhizomorphs through the soil, and it also spreads extensively up the trunks of dead trees by forming thick, black rhizomorphs beneath the bark. These rhizomorphs resemble boot laces, hence the common name for this fungus the boot-lace fungus. The main part of the rhizomorph has a fairly uniform thickness and is differentiated into zones: an outer cortex of thick-walled melanized cells in an extracellular matrix, a medulla of thinnerwalled, parallel hyphae, and a central channel where the medulla has broken down, serving a role in gaseous diffusion. Rhizomorphs branch by producing new multicellular apices, either behind the tip or by bifurcation of the tip. However, they need to be attached to a food base because their growth depends on translocated nutrients, so one of the traditional ways of preventing spread from tree to tree is by trenching of the soil to sever the rhizomorphs. Almost nothing is known about the developmental triggers of rhizomorphs, except that ethanol and other small alcohols can induce them; similarly, almost nothing is known about their mode of development because they originate deep within an established colony in laboratory culture. However, the behavior of rhizomorphs is of considerable interest, as shown by the work of Smith & Griffin (1971) on Armillariella (a) (b). In this fungus, the rhizomorph apex will only grow if it remains hyaline, and this means that the partial pressure of oxygen at the surface of the apex must be 0. Yet growth of the apex is strongly oxygen-dependent, and the fungus seems to resolve this dilemma by a combination of factors. A high respiration rate is maintained at the apex, supported partly by diffusion of oxygen along the central channel, while the surface of the apex is covered by a water film which limits the rate of oxygen diffusion: at 20°C, oxygen diffuses about 10,000 times more slowly through water than through air. The dependence on a water film ensures that rhizomorphs grow naturally at a specific depth in soil, depending on the soil type and the climate. If a tip grows too close to the soil surface then the width of the water film is reduced and oxygen diffuses to the tip more rapidly, causing melanization. These tips near to the soil surface then break down to produce "breathing pores" connected to the central channel. Conversely, if the apex grows too deeply into moist soil then the water film increases and the rate of growth becomes oxygen-limited. Thus, the peculiar organization of a rhizomorph helps to regulate growth to specific zones in the soil, and these zones are where tree roots occur, maximizing the opportunities for infection. Sporangiospores Sporangiospores are usually formed within a thinwalled sporangium, like the well-known sporangia of Mucor and other Zygomycota. Within a sporangium the nuclei undergo repeated mitotic divisions, then the cytoplasm is cleaved around the individual nuclei by the alignment and fusion of membranes. This is followed by production of a wall around each of the spores in the Zygomycota, or by the development of flagella in the wall-less spores of Chytridiomycota and Oomycota. Finally, the spores are released by controlled lysis of all or part of the sporangium wall.
The longitudinal membrane orientation and thin channel concentration chamber treatment uti discount 800 mg nootropil fast delivery, provide optimum cross flow conditions even for particle laden solutions; the centrifugal force pulling particles and solids away from the membrane to the bottom of the device symptoms 9 days after iui purchase nootropil toronto. Macromolecules collect in an impermeable concentrate pocket integrally moulded below the membrane surface 911 treatment cheap 800mg nootropil free shipping, thereby eliminating the risk of filtration to dryness symptoms 9 days after embryo transfer purchase nootropil visa. Device Vivaspin 15R Equipment required Centrifuge Rotor type Carrier Required 50 ml/30 mm d Vivaspin 15R Rotor compatibility Please note: Vivaspin 15R (30 mm +116 mm) is designed to fit into rotors that can accommodate Falcon 50 ml conical bottom tubes. These devices are not designed to fit into rotors that only accept round bottom 29 mm + 105 mm tubes. If your rotor accepts only 29 mm + 105 mm round bottom tubes, please use the Vivaspin 15, which can be used in either round bottom or conical centrifuge tubes. Swing bucket or Fixed angle Minimum rotor angle 25° Rotor cavity To fit 50 ml (30 mm) conical bottom tubes Concentrate recovery Fixed or variable Pipette type volume Recommended tip Thin gel loader type 2 Operation Operation 1. Fill concentrator with up to the maximum volumes shown in table 1 (Ensure screw closure is fully seated). Insert assembled concentrator into centrifuge (when fixed angle rotors are used, angle concentrator so that the top and window faces upwards outwards). Once the desired concentration is achieved, (see table 3 for guide to concentration times), remove assembly and recover sample from the bottom of the concentrate pocket with a pipette. Concentrate the sample again and repeat the process until the concentration of contaminating microsolute is sufficiently reduced. Recover Using the Vivaspin 15R Correct orientation in a fixed angle rotor Spin 3 Technical Specifications Table 1: Technical specifications Vivaspin 15R Concentrator capacity Swing bucket rotor Fixed angle rotor Dimensions Total length Width Active membrane area Hold up volume membrane Dead stop volume* Materials of construction Concentrator body Filtrate vessel Concentrator cap Membrane 15 ml 12. Expect significantly longer spin times for starting solutions with over 5% solids. Viscous solutions such as 50% glycerine will take up to 5 times longer to concentrate than samples in a predominantly buffer solution. Pre-rinsing Membranes fitted to Vivaspin concentrators contain trace amounts of Glycerine and Sodium azide. Should these interfere with analysis they can be removed by rinsing fill volume of buffer solution or deionised water through the concentrator. If you do not want to use the pre-rinsed device immediately, store it in the refrigerator with buffer or water covering the membrane surface. Sterilisation To sterilise, use a 70% ethanol solution or sterilising gas mixture. Chemical Compatibility Vivaspin concentrators are designed for use with biological fluids and aqueous solutions. This volume may vary depending on sample, sample concentration, operation temperature and centrifuge rotor. No part of this publication may be reprinted or translated in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Sartorius Lab Instruments GmbH & Co. The status of the information, specifications and illustrations in this manual is indicated by the date given below. The inhibitor chemically resembles a (one of the) substrate(s) and binds in the active site in the same way as the substrate(s) binds. The inhibitor, however, has a functional group, ususally a leaving group, that is replaced by a nucleophile in the enzyme active site. This covalent enzyme-inhibitor complex forms irreversibly, thereby irreversibly inactivating the enzyme. Therefore this type of inhibition is called "suicide inhibition" or affinity labeling and the inhibitor is called a "suicide inhibitor". This reaction with the suicide inhibitor removes active enzyme from the system; this removal is measured as inhibition. Since active enzyme is lost, the inhibition is not relieved at high substrate levels. The rate, at high substrate in the presence of the inhibitor,is still proportional to the amount of the enzyme-substrate complex. However, the maximum amount of that complex is limited by the remaining amount of active enzyme, not by the total enzyme added to the system. Review Article Curcumin and its protective and therapeutic uses Sudhanshu Agrawal1, Raj Kumar Goel2 1 2 Department of Physiology, Heritage Institute of Medical Sciences, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India. Department of Pharmacology, Heritage Institute of Medical Sciences, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India.
Skin contact with formaldehyde solution or inhalation of formaldehyde vapour should be avoided symptoms checker buy nootropil 800mg. Since stability is affected by concentration (and also by temperature and ph) treatment tinnitus best buy for nootropil, subsequent dilutions should be made only as needed and these solutions should be changed frequently (preferably each day treatment ear infection order nootropil 800 mg without a prescription, but at least weekly) medicine 3601 order 800mg nootropil. Simple garden-type spray bottles can be used for delivering hypochlorite solutions to surfaces prior to wiping down, although the chlorine will corrode the spring mechanism quite quickly and these spray bottles will need to be acquired and used on a semidisposable basis. Because of their neutralizing effect on chlorine, wooden benches should be replaced by more suitable materials or covered with plastic or laminated sheeting, or with a proprietary covering designed for the purpose, such as Benchcotet. Glass items should be transferred to a sharps container for autoclaving and/or incineration. Vertical surfaces should be washed or wiped down thoroughly with cloths soaked in this solution. Solutions of 10% formalin, 4% glutaraldehyde, 3% hydrogen peroxide or 1% peracetic acid are possible alternatives to hypochlorite, but the choice must be weighed against the greater personal protection needed when using these. Contaminated gowns/ aprons/coats should be removed immediately and placed in autoclave bins or bags and autoclaved. Personal clothing that may still be contaminated shoes, socks/stockings/upper garments if sleeves or collars are contaminated should be removed as soon as possible and, if possible, autoclaved. Alternatively, they may be fumigated in a cabinet or fumigation chamber (section 3. Bleach certainly should not be used on broken skin as it is likely to do more harm than good. Where the skin is broken (including needle-stick punctures), bleeding should be encouraged and the injury washed with copious amounts of water. For contamination of the mouth with Where possible, anthrax-contaminated materials to be disposed of, such as bedding, feedstuffs, manure, etc. Probably a way of neutralizing and degassing the fumigant should be worked out in advance of taking this route. Certain bacteria and yeast are also able to bring about this degradation by means of dehydrogenases. An alkaline ph neutralizes the formic acid and thereby increases the rate of degradation by pulling the equilibrium in that direction. Buffering or addition of lime, to counteract the lowered ph as formic acid is produced, will aid degradation. Filtration, as for water treatment, is probably effective as far as the emerging water is concerned, but leaves unsolved the problem of contaminated filter beds. Autoclaving is the surest way of killing spores but is only applicable to fairly small volumes of water. Where it is necessary to decontaminate soil to greater depths, such as burial sites of anthrax carcasses, 10% formalin should be injected below the soil surface at a rate of 30 ml for every 10 cm of depth at 0. Where it is not feasible to incinerate or chemically decontaminate the soil or to remove it to an incinerator, the alternative is to close or seal off the site. Covering with concrete or tarmac for, say, a car park, is an alternative used in industrialized countries; planting with thorny bushes surrounded by a secure fence can be an aesthetic approach. Calculations of exposure times need to take into account the size and density of the bales being irradiated. Where possible, contaminated materials should be incinerated or autoclaved at 121 °C for 60 minutes. Where possible these should be decontaminated by fumigation (formaldehyde or ethylene oxide) or by irradiation prior to processing. Control processes in tanneries should therefore be primarily targeted at stages before dehairing, particularly dust control and treatment of effluent from initial washing and rehydrating stages. Peracetic acid (3%) for > 30 minutes is an alternative but more expensive treatment. Precautions should be taken to avoid crosscontamination of hides and skins pre- and post-treatment through appropriate controls on movement of personnel, equipment and the hides themselves. Similarly, bonemeal in fertilizers is periodically suspected of being the source of anthrax infection in humans and animals. Similarly it should be a reasonable policy aim in any country to collect and process separately those raw bone, hoof and horn products obtained from regular and supervised slaughtering and those obtained from sources of uncertain origin, which present a higher risk in terms of anthrax. Long-term control will be dependent on improved and effective control measures in the exporting countries.
Order 800 mg nootropil otc. Heart attack survivor says doctors blamed symptoms on anxiety.