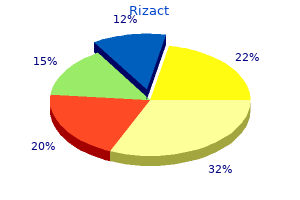
"Purchase rizact cheap, allied pain treatment center ohio".
By: R. Redge, M.A.S., M.D.
Assistant Professor, University of New Mexico School of Medicine
Navigational Note: Hypersomnia Mild increased need for sleep Moderate increased need for Severe increased need for sleep sleep Definition: A disorder characterized by characterized by excessive sleepiness during the daytime advanced pain treatment center jackson tn generic rizact 5 mg mastercard. Navigational Note: Ischemia cerebrovascular Asymptomatic; clinical or Moderate symptoms diagnostic observations only; intervention not indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease or absence of blood supply to the brain caused by obstruction (thrombosis or embolism) of an artery resulting in neurological damage shoulder pain treatment yahoo cheap rizact online mastercard. Symptoms include an increase in the muscle tone in the lower extremities pain treatment goals cheap rizact 10 mg with mastercard, hyperreflexia hip pain treatment options order rizact with mastercard, positive Babinski and a decrease in fine motor coordination. Patients experience marked discomfort radiating along a nerve path because of spinal pressure on the connecting nerve root. Navigational Note: Recurrent laryngeal nerve Asymptomatic; clinical or Moderate symptoms Severe symptoms; medical Life-threatening Death palsy diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated. It has been observed in association with hypertensive encephalopathy, eclampsia, and immunosuppressive and cytotoxic drug treatment. Navigational Note: Spasticity Mild or slight increase in Moderate increase in muscle Severe increase in muscle Life-threatening Death muscle tone tone and increase in tone and increase in consequences; unable to resistance through range of resistance through range of move active or passive range motion motion of motion Definition: A disorder characterized by increased involuntary muscle tone that affects the regions interfering with voluntary movement. Navigational Note: Syncope Fainting; orthostatic collapse Definition: A disorder characterized by spontaneous loss of consciousness caused by insufficient blood supply to the brain. Navigational Note: Tendon reflex decreased Ankle reflex reduced Ankle reflex absent; other Absence of all reflexes reflexes reduced Definition: A disorder characterized by less than normal deep tendon reflexes. Navigational Note: Vasovagal reaction Present Life-threatening Death consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a sudden drop of the blood pressure, bradycardia, and peripheral vasodilation that may lead to loss of consciousness. Navigational Note: Premature delivery Grade 4 <1% percentile of weight for gestational age Grade 5 - Fetal loss at any gestational age - Delivery of a liveborn infant at Delivery of a liveborn infant at Delivery of a liveborn infant at Delivery of a liveborn infant at >34 to 37 weeks gestation >28 to 34 weeks gestation 24 to 28 weeks gestation 24 weeks of gestation or less Definition: A disorder characterized by delivery of a viable infant before the normal end of gestation. Typically, viability is achievable between the twentieth and thirty-seventh week of gestation. Navigational Note: Anorgasmia Inability to achieve orgasm Inability to achieve orgasm not adversely affecting adversely affecting relationship relationship Definition: A disorder characterized by an inability to achieve orgasm. Navigational Note: Delayed orgasm Delay in achieving orgasm not Delay in achieving orgasm adversely affecting adversely affecting relationship relationship Definition: A disorder characterized by sexual dysfunction characterized by a delay in climax. Navigational Note: Delusions Moderate delusional Severe delusional symptoms; Life-threatening Death symptoms hospitalization not indicated; consequences, threats of new onset harm to self or others; hospitalization indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by false personal beliefs held contrary to reality, despite contradictory evidence and common sense. Navigational Note: Euphoria Mild mood elevation Moderate mood elevation Severe mood elevation. Navigational Note: Insomnia Mild difficulty falling asleep, Moderate difficulty falling Severe difficulty in falling staying asleep or waking up asleep, staying asleep or asleep, staying asleep or early waking up early waking up early Definition: A disorder characterized by difficulty in falling asleep and/or remaining asleep. Navigational Note: Libido decreased Decrease in sexual interest Decrease in sexual interest not adversely affecting adversely affecting relationship relationship Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in sexual desire. Navigational Note: Libido increased Present Definition: A disorder characterized by an increase in sexual desire. Navigational Note: Psychosis Mild psychotic symptoms Moderate psychotic Severe psychotic symptoms Life-threatening Death symptoms. Navigational Note: Also consider Investigations: Creatinine increased Bladder perforation Invasive intervention not Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death indicated indicated consequences; organ failure; urgent operative intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a rupture in the bladder wall. Navigational Note: Bladder spasm Intervention not indicated Antispasmodics indicated Hospitalization indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by a sudden and involuntary contraction of the bladder wall. For grades higher than Grade 1, consider Renal and urinary disorders: Bladder spasm or Cystitis noninfective; Infections and infestations: Urinary tract infection. Navigational Note: Hemoglobinuria Asymptomatic; clinical or diagnostic observations only; intervention not indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate the presence of free hemoglobin in the urine. Navigational Note: Proteinuria 1+ proteinuria; urinary protein Adult: 2+ and 3+ proteinuria; Adult: Urinary protein >=3. Navigational Note: Renal hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Analgesics and hematocrit Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death not indicated monitoring indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by bleeding from the kidney. Navigational Note: Urinary fistula Symptomatic, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent invasive intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between any part of the urinary system and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Urinary tract obstruction Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic but no Altered organ function.
These researchers suggest that marital counseling be a routine part of the treatment of depressives who are married knee pain treatment video cheap rizact 5mg without prescription. People who have few friends and who are involved in few social activities are more prone to being depressed (Barnett & Gotlib pain diagnostic treatment center sacramento ca buy rizact from india, 1988) pain and spine treatment center dworkin buy rizact mastercard. Lack of social integration reduces the opportunities for engaging in pleasant events xiphisternum pain treatment rizact 10mg overnight delivery, reduces the number of sources of help, and allows people who ruminate on their distress to become further withdrawn and depressed. Discuss with students the circumstances that have surrounded depression in their own lives and the roles that family members, friends, and other help providers have played in reducing or Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. What level of social integration did they experience before, during, and after the depressive episode? Psychosocial functioning and depression: Distinguishing among antecedents, concomitants and consequences. To indicate the spectrum of mood disorders, draw a long horizontal line on the blackboard and label the poles "Psychotic Depression" and "Delirious Mania". Then indicate a region toward the middle of the continuum that represents normal fluctuations in mood. Make only dotted lines to indicate the hazy boundaries separating "normal" behaviors and clinical disorders. Ask students to describe mild to moderate depression and list the affective, cognitive, behavioral, and physiological symptoms they suggest. In this region of the diagram, note dysthymia (based on closeness to "normal" and duration) and both exogenous and endogenous major depressions. On the mania side of normal, describe hypomania and then acute and delirious mania. The area from neurotic depression to hypomania can then be linked by a double-headed arrow to show cyclothymia. Finally, the bigger mood swings of bipolar disorder can be indicated by an even larger doubleheaded arrow. It may be helpful to students to organize these categories in the following way: First is the psychotic versus neurotic dimension. Unlike many other forms of disorders, the mood disorders raise the issue of continuity (from "neurotic" conditions to psychotic ones). Third, particularly with the depressions, are the exogenous and endogenous explanations. Fourth, some disorders are mild and prolonged (cyclothymia and dysthymia), whereas others are severe and perhaps more acute (major depression and bipolar disorders). Finally, some mood disorders are primary (unaccompanied by other mental disturbances), whereas many are secondary (the outgrowth or a concomitant feature of some other disorder). You should remind students that the categorization of disorders is often overly neat and tidy. Many people with drinking or other substance abuse problems experience serious depressive episodes. A diagnosis of secondary depression may be more accurate, but figuring out which came first is a very difficult proposition. The spiral includes poor social skills, reduced reinforcement, lowered activity, and worsening depressive symptoms. Treatment argues that an upward spiral of increased activity, increased reinforcement, and increased social skill and mood is also possible. The reasons for the reported sex differences in depression are many and controversial. One reason is that men and women are socialized to express emotions differently and are taught to expect different reactions from others when they are distressed. The following exercise may reveal to students norms for experiencing depression and coping with it. Set up small groups (six to eight per group) with even numbers of males and females. Try to visualize where you were, what you were doing, and how others were responding to you.
Hyperthyroidism secondary to thyroiditis (with release of preformed hormone into the circulation) or an extrathyroidal source of thyroid hormone neuropathic pain treatment guidelines and updates 5mg rizact amex. Causes include G Thyroiditis: painless and postpartum thyroiditis allied pain treatment center boardman oh buy 10 mg rizact mastercard, subacute painful or de Quervain thyroiditis (see Chapter 5 pain treatment in dvt buy discount rizact 5 mg line. Head and Neck 473 N Treatment Options the treatment depends on the cause of thyrotoxicosis pain management for arthritis in dogs rizact 10 mg generic. Medical Beta blockers such as propranolol or atenolol provide symptomatic relief in all types of hyperthyroidism. Antithyroid drugs are used for primary therapy of thyrotoxicosis, for attainment of euthyroidism in preparation for thyroidectomy, and for use in conjunction with radioiodine therapy in selected patients. Permanent hypothyroidism likely; pregnancy and breast-feeding should be avoided until after 6 to 12 months. Surgery Thyroidectomy or subtotal thyroidectomy is usually curative but results in iatrogenic hypothyroidism; risks include potential injury to parathyroids and recurrent laryngeal nerve. Orbital decompression may be necessary in patients with severe Graves ophthalmopathy. N Outcome and Follow-Up the outcome depends on the cause of hyperthyroidism and the treatment modality. Primary hypothyroidism: the thyroid gland produces insufficient amounts of thyroid hormone. N Etiology Primary Hypothyroidism Primary hypothyroidism accounts for G 99% of cases. Iatrogenic disease: Thyroidectomy, radioiodine treatment, and external radiotherapy. Head and Neck G 475 G Iodine deficiency and iodine excess: Both can cause hypothyroidism. Other drugs that can cause hypothyroidism include amiodarone, lithium carbonate, interleukin-2, and interferon alfa. Transient hypothyroidism: this can occur during the course of several types of thyroiditis, followed by recovery of thyroid function. Some patients who undergo subtotal thyroidectomy become hypothyroid after 4 to 8 weeks, but recover several weeks or months later. Hypothyroidism in infants and children: the most common causes of congenital hypothyroidism are agenesis and dysgenesis of the thyroid, but a few are delivered by mothers who were receiving an antithyroid drug for hyperthyroidism. Among children who become hypothyroid later, the most common cause is chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. G G Central (Secondary and Tertiary) Hypothyroidism Central (secondary and tertiary) hypothyroidism can be caused by: G G Most often a pituitary tumor (macroadenomas), pituitary surgery, or irradiation Less common causes are head injury, postpartum pituitary necrosis (Sheehan syndrome), pituitary apoplexy (bleeding in a pituitary tumor), hypophysitis, nonpituitary tumors such as craniopharyngiomas and infiltrative diseases Tissue Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Tissue resistance to thyroid hormone is rare. N Epidemiology Primary hypothyroidism is a common disease worldwide in both iodinedeficient and replete regions. Mean age at diagnosis in women is 60 years with increasing occurrence with advancing age. N Clinical Deficiency of thyroid hormone causes a generalized slowing of metabolic processes and/or accumulation of matrix glycosaminoglycans in the interstitial spaces of many tissues. Symptoms Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, myalgia, cold intolerance, weight gain, depression, cognitive dysfunction, mental retardation (in infants), constipation, menstrual irregularity, hair loss, and hoarseness. In this setting, differentiation must be made between pituitary and hypothalamic disorders. Hyperlipidemia occurs with increased frequency in hypothyroidism; as a result, patients with dyslipidemia should be screened for thyroid dysfunction. Thyroid function should be measured in all patients with unexplained hyponatremia, as this is another laboratory manifestation of hypothyroidism. Thyroid function should also be measured in patients undergoing evaluation for high serum muscle enzyme concentrations or anemia. Head and Neck 477 Special treatment situations for hypothyroidism include: G Elderly patients or those with known or suspected heart disease: these patients should initially be treated with low doses of levothyroxine 25 g/day. Hypothyroidism during pregnancy: Women require more thyroid hormone during pregnancy. Surgical patients: Urgent surgery should not be postponed in hypothyroid patients. Patients receiving chronic T4 therapy who undergo surgery and are unable to eat for several days need not be given T4 parenterally.
Gyri and sulci (fissures) · In the fourth month long island pain treatment center generic rizact 10mg with visa, no gyri or sulci are present; the brain is smooth or lissencephalic laser pain treatment reviews order generic rizact pills. Schematic drawings illustrating a variety of neural tube defects involving the spinal cord pain treatment center richmond ky order 10mg rizact overnight delivery. The term spina bifida applies to all of the defects because the bony arch of one or more vertebrae has failed to fuse dorsal to the spinal cord pain treatment and wellness center pittsburgh cheap rizact express. Anencephaly (meroanencephaly) · results from failure of the anterior neuropore to close. Ossification defects of the occipital bone (Figure 4-13) · are also called cranium bifidum. Schematic drawings illustrating the various types of occipital encephaloceles (cranium bifidum). Arnold-Chiari malformation (Figures 4-14 and 4-15) · is a cerebellomedullary malformation in which the caudal vermis, cerebellar tonsils, and medulla herniate through the foramen magnum, resulting in an obstructive hydrocephalus. Microgyri Lateral ventricle Corpus callosum Third ventricle Aqueductal stenosis Tectal (quadrigeminal) plate Fourth ventricle Herniation of vermis Herniation of medulla Figure 4-15 Arnold-Chiari malformation, midsagittal section, T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scan. Dandy-Walker syndrome (Figure 4-16) · consists of a huge cyst of the posterior fossa associated with atresia of the outlet foramina of Luschka and Magendie. Lateral ventricle Third ventricle/ thalamus Cerebral aqueduct Confluence of sinuses Cerebellar vermis Chiasm Posterior fossa cyst Mamillary body A B Figure 4-16. An enormous dilation of the fourth ventricle results from failure of the foramina of Luschka and Magendie to open. This condition is associated with occipital meningocele, elevation of the confluence of the sinuses (torcular Herophili), agenesis of the cerebellar vermis, and splenium of the corpus callosum. Fetal alcohol syndrome · includes growth retardation, microcephaly, and congenital heart anomalies. Aqueductal stenosis is the most common cause of congenital hydrocephalus; it may be transmitted by an X-linked trait or may be caused by cytomegalovirus infection or toxoplasmosis. Noncommunicating hydrocephalus results from obstruction within the ventricle system. Holoprosencephaly (Figure 4-18) · results from failure of midline cleavage (diverticularization) of the embryonic forebrain. Lateral ventricle (body) Third ventricle Hydrocephalus Lateral ventricle (temporal horn) Porencephaly False porencephaly Hydranencephaly Figure 4-17. Holoprosencephaly results from failure of midline cleavage of the embryonic prosencephalon. It may result from alcohol abuse, especially during the first 4 weeks of pregnancy. Polyhydramnios · is an excess of amniotic fluid, resulting from the inability of the fetus to swallow amniotic fluid. Hydranencephaly (see Figure 4-17) · is a congenital absence of cerebral hemispheres, which are replaced by hugely dilated ventricles. Porencephaly (see Figure 4-17) · is cystic cavitation of the prosencephalon due to agenesis of the cortical mantle. False porencephaly (see Figure 4-17) · is a malformation consisting of cystic cavities that are lined with glia and do not communicate with the lateral ventricle. Tethered spinal cord (filum terminale syndrome) · results from a thick, short filum terminale. Gives rise to the solitary nucleus Questions 10 to 14 Match the statements in items 10 to 14 with the appropriate lettered structure shown in the figure. The neural retina is derived from the alar plate choroid neural crest neural tube telencephalic vesicle wall 2. Caudal herniation of the cerebellar tonsils and medulla through the foramen magnum is called (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Dandy-Walker syndrome Down syndrome Arnold-Chiari syndrome cranium bifidum myeloschisis A B E D C 4. Gives rise to motor neurons that migrate into the lateral pontine tegmentum Questions 5 to 9 Match the statements in items 5 to 9 with the appropriate lettered structure shown in the figure. Arnold-Chiari syndrome is a cerebellomedullary malformation in which the inferior vermis and medulla herniate through the foramen magnum, resulting in communicating hydrocephalus.
Buy discount rizact 10mg online. Back pain relief thanks to Salem Hospital Spine Center of Excellence.