"Order spirulina pills in toronto, treatment whooping cough".
By: V. Kulak, MD
Clinical Director, University of Missouri–Kansas City School of Medicine
A physician may develop a donor site at a location far away from the recipient site medicine interactions discount spirulina 500mg otc. The graft code can be assigned more than once when the surgery is performed in stages medications that cause tinnitus purchase spirulina online from canada. Notes specific to this group of codes state that when reporting transfer flaps (in several stages) medicine 3 sixes discount 500mg spirulina overnight delivery, report the donor site when a tube graft treatment resistant schizophrenia generic spirulina 500 mg amex. B, Intermediate inset of the tube flap following separation from its abdominal blood supply. This process of "waltzing" or "walking" a tube-flap from the abdomen to the chest was used by Halsted and Billroth. D, the lateral half of the tube flap was then detached laterally and inset into the upper sternum to create the breast shape. This type of reconstruction usually took more than a year to complete, with more than a dozen procedures. Separate subcutaneous pedicle transposition flap is designed to resurface the alar lobule after placement of auricular cartilage graft (arrows) along the missing alar margin. In a delayed graft, a portion of the skin is lifted and separated from the tissue below, but it stays connected to blood vessels at one end. This keeps the skin viable while it is being moved from one area to another, and at the same time, it allows the graft to get used to living on a small supply of blood. It is hoped that living on a small blood supply will give the graft a better chance of survival when inserted into the recipient site. The first category, Flaps (Skin and/or Deep Tissues) (15570-15738), is subdivided based on the type of flap. The codes do not include any extensive immobilization that may be necessary, such as a large plaster cast. Also not included in the flap procedure codes is the closure of a donor site, which would be reported in addition to the flap procedure. The second category, Other Flaps and Grafts (15740-15777), is subdivided based on the type of flap (free muscle, free skin, fascial, or hair transplant). Within the flap codes (15740-15750) the flap (donor site and recipient site remain connected for a period of time) can be an island pedicle or a neurovascular pedicle. An island pedicle flap contains an artery and vein, and a neurovascular pedicle flap contains an artery, vein, and nerve. The term "island" refers to the removal of the fat and subcutaneous tissue prior to implantation into the recipient site. The neurovascular pedicle flap is used when the area of defect requires restoration of sensation in the area; for example, the end of a finger that has sustained damage that destroyed the sensation on the tip of the finger. A neurovascular graft from an adjacent finger could restore sensation to the defective area. The connection between the donor and the recipient sites remains in place until the graft has satisfactorily healed, at which time the connection is severed. The donor area may require a separate skin graft, and that graft would be reported separately. Wound Repair (Answers are located in Appendix C) Other procedures the Other Procedures codes (15780-15879) report a wide variety of repair services, such as abrasion, chemical peel, and blepharoplasty (surgical reconstruction of the eyelid). Dermabrasion is used to treat acne, wrinkles, or general keratoses (horny growth). The skin area is anesthetized by a chemical that freezes the area (a cryogen), and the area is sanded down using a motorized brush. The facial dermabrasion codes (1578015781) are divided according to the surface area of the face treated (total, segmental). The process involves the use of a high-speed mechanical wheel to remove the epidermis and part of the papillary dermis. The abrasion codes (15786, 15787) report the use of abrasion to remove a lesion, such as scar tissue, a wart, or a callus. The first abraded lesion is reported with 15786, and each additional four or fewer lesions are reported with 15787. Chemical peels, also known as chemexfoliation, are treatments in which a chemical is applied to the skin and then removed.
Fetal infection can occur at any time during pregnancy medicine hat lodge order spirulina master card, but early-gestation infection may result in multiple organ anomalies medicine for vertigo 500mg spirulina for sale. When maternofetal transmission occurred during the first 10 weeks of gestation treatment diarrhea buy spirulina no prescription, 100% of the infected fetuses had cardiac defects and deafness medicine 7 order spirulina 500mg with amex. Deafness was found in one-third of fetuses infected at 13 to 16 weeks, but no abnormalities were found when fetal infection occurred beyond the 20th week of gestation. The most common cardiac defects are patent ductus arteriosus and pulmonary artery stenosis. A 20-year follow-up study of 125 patients with congenital rubella from the 1960s epidemic found ocular disease to be the most common disorder (78%), followed by sensorineural hearing deficits (66%), psychomotor retardation (62%), cardiac abnormalities (58%), and mental retardation (42%). This is necessary because the clinical symptoms of rubella are nonspecific and can be seen with infection by other viral agents. Several sensitive and specific assays exist for the detection of rubella-specific antibody. Viral isolation from the nose, throat, and/or urine is possible, but this is costly and not practical in most instances. Symptoms typically begin 2 to 3 weeks after exposure and include malaise, low-grade fever, headache, mild coryza, and conjunctivitis occurring 1 to 5 days before the onset of rash. The rash is a salmon-pink macular or maculopapular exanthem that begins on the face and behind the ears and spreads downward over 1 to 2 days. The rash disappears in 5 to 7 days from onset, and posterior cervical lymphadenopathy is common. In women suspected of having acute rubella infection, confirmation can be made by demonstrating a fourfold or higher rise in serum IgG titers when measured at the time of symptoms and approximately 2 weeks later. The results of some assays may not directly correlate with a fourfold rise in titer, so other criteria for a significant increase in antibody may be required. When there is uncertainty about the interpretation of assay results, advice should be obtained from the laboratory running the test and an infectious diseases consultation. Any individual known to have been immunized with rubella vaccine after his or her first birthday is generally considered immune. However, it is best to determine immunity by measuring rubella-specific IgG, which has become a standard of practice in obstetric care. If a woman exposed to rubella is known to be seropositive, she is immune, and the fetus is considered not to be at risk for infection. Reinfections in previously immune women have been rarely documented, but the risk of fetal damage appears to be very small. If the exposed woman is known to be seronegative, a serum sample should be obtained 3 to 4 weeks after exposure for determination of titer. A negative titer indicates that no infection has occurred, whereas a positive titer indicates infection. Women with an uncertain immune status and a known exposure to rubella should have serum samples obtained as soon as possible after exposure. If this is done within 7 to 10 days of exposure, and the titer is positive, the patient is rubella immune and no further testing is required. If the first titer is negative or was determined on serum taken more than 7 to 10 days after exposure, repeat testing (3 weeks later) and careful clinical follow-up are necessary. When both the immune status and the time of exposure are uncertain, serum samples for titer determination should be obtained 3 weeks apart. Alternatively, infection is confirmed if seroconversion or a fourfold increase in titer is observed. Further testing and close clinical follow-up are required if titer results are inconclusive. It should be emphasized that all serum samples should be tested simultaneously by the same laboratory when one is determining changes in titers with time. This can be accomplished by saving a portion of each serum Infectious Diseases 621 sample before sending it for titer determination.
Spirulina 500 mg otc. My lovely English.
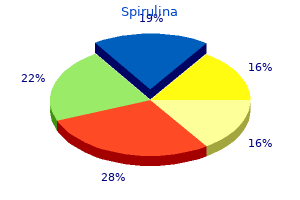
Vincae minoris herba (Periwinkle). Spirulina.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Periwinkle work?
- Preventing brain disorders, tonsillitis, sore throat, intestinal swelling (inflammation), toothache, chest pain, wounds, high blood pressure, and other conditions.
- What is Periwinkle?
- Dosing considerations for Periwinkle.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96484
This rash may be pruritic medicine wheel spirulina 500mg amex, does not desquamate symptoms 7 days before period spirulina 500mg discount, and may recur with exercise medications jamaica purchase line spirulina, bathing medications lisinopril buy spirulina without a prescription, rubbing, or stress. Adolescents and adults may experience myalgia, significant arthralgias or arthritis, headache, pharyngitis, coryza, and gastrointestinal upset. Most children with parvovirus B19-induced transient aplastic crisis have multiple symptoms, including fever, lethargy, malaise, pallor, headache, gastrointestinal symptoms, and respiratory symptoms. The reticulocyte count is extremely low, and the hemoglobin level is lower than usual for the patient. Parvovirus B19 is not teratogenic, but in utero infection of fetal erythroid cells may result in fetal heart failure, hydrops fetalis, and fetal death. Of the approximately 50% of women of childbearing age susceptible to parvovirus B19 infection, 30% of exposed women develop infection, with 25% of exposed fetuses becoming infected and 10% of these culminating in fetal death. Exclusion of affected children from school is not recommended, because children generally are not infectious by the time the rash is present. Good handwashing and hygiene are practical measures that should help reduce transmission. Any branch of cranial nerve V may be involved, which also may cause corneal and intraoral lesions. Ophthalmic zoster may be associated with ipsilateral cerebral angiitis and stroke. Immunocompromised persons may have unusually severe, painful herpes zoster that involves cutaneous and, rarely, visceral dissemination (to liver, lungs, and central nervous system). Postherpetic neuralgia, defined as pain persisting longer than 1 month, is uncommon in children. It disseminates by a primary viremia and infects regional lymph nodes, the liver, the spleen, and other organs. A secondary viremia follows, resulting in a cutaneous infection with the typical vesicular rash. After resolution of chickenpox, the virus persists in latent infection in the dorsal root ganglia cells. Chickenpox is highly communicable in susceptible individuals, with a secondary attack rate of more than 90%. The period of communicability ranges from 2 days before to 7 days after the onset of the rash, when all lesions are crusted. Epidemiology Laboratory and Imaging Studies In the prevaccine era, the peak age of occurrence was 5 to 10 years, with peak seasonal infection in late winter and spring. In the postvaccine era, the incidence of varicella has declined in all age groups, with the peak incidence now in 10 to 14 year olds. The overall incidence of zoster (215 cases per 100,000 person-years) results in a cumulative lifetime incidence of approximately 10% to 20%, with 75% of cases occurring after 45 years of age. Differential Diagnosis Clinical Manifestations Decision-Making Algorithms Available @ StudentConsult. The characteristic rash appears initially as small red papules that rapidly progress to nonumbilicated, oval, "teardrop" vesicles on an erythematous base. The fluid progresses from clear to cloudy, and the vesicles ulcerate, crust, and heal. New crops appear for 3 to 4 days, usually beginning on the trunk followed by the head, the face, and, less commonly, the extremities. There may be a total of 100 to 500 lesions, with all forms of lesions being present at the same time. The severity of the rash varies, as do systemic signs and fever, which generally abate after 3 to 4 days. The preeruption phase of zoster includes intense localized and constant pain and tenderness (acute neuritis) along a dermatome, accompanied by malaise and fever. In several days, the eruption of papules, which quickly vesiculate, occurs in the dermatome or in two adjacent dermatomes. Groups of lesions the diagnosis of varicella and zoster is based on the distinctive characteristics of the rash. Coxsackievirus A infection has a vesiculopustular appearance, but lesions are usually localized to the extremities and oropharynx.
The pieces of solid matter are not taken out Bypass Change Includes/Examples: Definition: Control Creation Destruction Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Detachment Dilation Division Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Drainage Excision Extirpation Extraction Fragmentation Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy medications used to treat adhd generic spirulina 500 mg otc, transurethral lithotripsy Fusion Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Insertion Inspection Map Occlusion Reattachment Release Removal of device from Repair Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Replacement Reposition Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Resection Restriction Revision Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Explanation: Includes/Examples: Definition: Joining together portions of an articular body part rendering the articular body part immobile the body part is joined together by fixation device medicine for constipation buy discount spirulina 500mg on-line, bone graft treatment yeast infection women 500mg spirulina with visa, or other means Spinal fusion medications beta blockers purchase spirulina with a visa, ankle arthrodesis Putting in a nonbiological appliance that monitors, assists, performs, or prevents a physiological function but does not physically take the place of a body part N/A Insertion of radioactive implant, insertion of central venous catheter Visually and/or manually exploring a body part Visual exploration may be performed with or without optical instrumentation. A Removal procedure is coded for taking out the device used in a previous replacement procedure Total hip replacement, bone graft, free skin graft Moving to its normal location or other suitable location, all or a portion of a body part the body part is moved to a new location from an abnormal location, or from a normal location where it is not functioning correctly. The body part may or may not be cut out or off to be moved to the new location Reposition of undescended testicle, fracture reduction Cutting out or off, without replacement, all of a body part N/A Total nephrectomy, total lobectomy of lung Partially closing the orifice or lumen of a tubular body part the orifice can be a natural orifice or an artificially created orifice Esophagogastric fundoplication, cervical cerclage Correcting, to the extent possible, a portion of a malfunctioning or the position of a displaced device Explanation: Supplement Revision can include correcting a malfunctioning or displaced device by taking out and/or putting in a part of the device Includes/Examples: Adjustment of position of pacemaker lead, recementing of hip prosthesis Definition: Putting in or on biologic or synthetic material that physically reinforces and/or augments the function of a portion of a body part Explanation: the biological material is non-living, or is living and from the same individual. The body part may have been previously replaced, and the Supplement procedure is performed to physically reinforce and/or augment the function of the replaced body part Includes/Examples: Herniorrhaphy using mesh, free nerve graft, mitral valve ring annuloplasty, put a new acetabular liner in a previous hip replacement Transfer Definition: Moving, without taking out, all or a portion of a body part to another location to take over the function of all or a portion of a body part Explanation: the body part transferred remains connected to its vascular and nervous supply Includes/Examples: Tendon transfer, skin pedicle flap transfer Transplantation Definition: Putting in or on all or a portion of a living body part taken from another individual or animal to physically take the place and/or function of all or a portion of a similar body part Explanation: the native body part may or may not be taken out, and the transplanted body part may take over all or a portion of its function Includes/Examples: Kidney transplant, heart transplant A closer look at root operations. The root operation is described by one of the main terms, as outlined on page 708 in Table 27-1. These root operations can be grouped into types of operations, such as operations that always involve devices: insertion, replacement, removal, change. Codes may also be located in the Index by specific procedures such as X-ray-see Imaging. The Index refers you to a specific entry in the Tabular List by providing the first three or four digits of the procedure code. It is always necessary to refer to the Tabular List to obtain the complete code because the Index contains only the first few numbers and letters. The tabular list completes the code the Tabular List provides the remaining characters needed to complete the code listed in the Index. The Tabular List is arranged by sections, and most sections are subdivided by body systems. For each body system, the Tabular List begins with a list of the operations performed, that is, the root operations. For example, a section of the listing of operations performed in respect to the central nervous system is as follows: Bypass Change Destruction Division Drainage Excision the Tabular List for each body system also includes a list of the body parts, approaches, devices, and qualifiers for that system. At the top of each of the tables is the name of the section, body system, and root operation as well as the definition of the root operation. The four columns in the grid represent the last four characters of the code (which are labeled Body Part, Approach, Device, and Qualifier in the Obstetrics and Medical and Surgical sections). Each row in the grid specifies the allowable combinations of the last four characters. If you choose the character 0, Products of Conception, you must continue to choose from the available numbers or letters in that same line. Chapter 27 learning objective review Review the Chapter Learning Objectives located at the beginning of the chapter, then answer the following questions that relate to each objective (Answers are located in Appendix E): 1 What services are referred to as "professional" services InpatientOutpatient 2 In which setting can any confirmed or definitive diagnoses be coded from the interpretation of a diagnostic test result TrueFalse 6 In the inpatient setting, the physician documents suspected cholelithiasis in the discharge summary. TrueFalse 8 A patient is admitted with low-grade fever and right upper quadrant pain. TrueFalse 14 An example of a procedure that involves inspection is: a gastrojejunal bypass b control of postprocedural bleeding c diagnostic arthroscopy d incision and drainage of abscess 15 Altering the route of passage of the contents of a tubular body part is a. Patient was found to have both pneumonia and decompensated congestive heart failure. Online resources the Evolve Learning Resources offer helpful material that will extend your studies beyond the classroom. Practice exercises have been provided for extra practice using TruCode and are located in the TruCode Resources folder on Evolve. Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting, Content Updates, and Coding links help you stay current with this ever-changing field. Online Activities and Chapter Review applications provide electronic assessment options (though answers are still only provided at the discretion of the instructor). Osteoarthritis is not reported because it has not been confirmed and is a "rule out" diagnosis. Carpal tunnel syndrome is not reported because the condition has not been confirmed, rather it is a "probable" condition. Abdominal pain, nausea and sometimes vomiting, loss of appetite, low-grade fever, constipation, diarrhea, inability to pass gas, abdominal swelling (any two of these) 2. When referencing Cardiomyopathy as the main term and amyloid as the subterm in the Index of the I-10, the coder is directed to report I43 by the placement of I43 in brackets following E85.