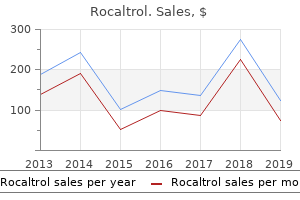
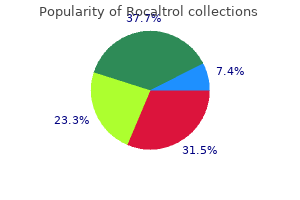
"Rocaltrol 0.25 mcg fast delivery, symptoms ketosis".
By: F. Gnar, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Co-Director, Cooper Medical School of Rowan University
These rare complications include acute pericarditis; tracheal symptoms 8dpiui order rocaltrol 0.25mcg amex, bronchial medicine youth lyrics purchase rocaltrol 0.25 mcg without a prescription, or esophageal obstruction; esophageal diverticuli; bronchoesophageal fistula; broncholithiasis (secondary to erosion of a calcification into a bronchus); mediastinal granuloma; mediastinal fibrosis or fibrosing mediastinitis; and enlarging histoplasmoma (usually located in the peripheral lung parenchyma and recognized by concentric laminations of calcium) treatment 12th rib syndrome generic rocaltrol 0.25mcg otc. Mediastinal granuloma treatment kidney failure buy rocaltrol 0.25mcg visa, which tends to develop more often in the right paratracheal area, is more circumscribed, smaller in size, and associated with fewer sequelae than is mediastinal fibrosis. Chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis often resembles pulmonary tuberculosis in symptomatology and radiographic manifestations, although the course of this type of histoplasmosis tends to be milder and more indolent than that of tuberculosis. The pathogenesis and course of chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis are highly complex; pathologic studies indicate two basic lesions. An interstitial pneumonitis is characteristic of the early lesion, whereas the chronic lesion is manifested by organization of diseased tissue, with prominence of giant cells and progressive cavitation. In the thicker-walled cavities, infection is persistent, with continuing necrosis, leading to progressive cavity enlargement (marching cavity) at the expense of the surrounding lung parenchyma. In general, the symptoms and roentgenographic findings reflect the two types or stages of disease, namely, pneumonitis and progressive cavitation. Although symptoms overlap, they tend to be more abrupt in onset, with more severe constitutional symptoms, such as fever, night sweats, and malaise, in the pneumonitis stage; hemoptysis and progressive dyspnea are more typical of the cavitation stage. In 80% of cases, the pneumonitis stage tends to resolve spontaneously over 2 to 3 months, with a small fibrotic residuum, whereas the cavitation stage, especially that associated with thick-walled cavities, tends to be relentlessly progressive, leading to destruction and diminution of lung parenchyma, fibrosis, and, eventually, respiratory insufficiency. The severity of the symptoms and signs of disseminated disease and the attendant histopathologic findings in a given patient mirror the level of immunocompetence of the individual. For example, in patients with the mildest and most chronic forms of disseminated disease, well-developed tuberculoid granulomas, typical of the response in normal hosts, can be found in reticuloendothelial tissues. Fever, chills, and other nonspecific constitutional symptoms, including malaise and weight loss, predominate. On initial presentation, many patients satisfy criteria for fever of unknown origin. Enlargement of liver and spleen is common; less frequently, peripheral lymphadenopathy is present. Mucous membrane ulceration, especially of the oropharynx, occurs in about 25 to 75% of patients with subacute disease and should alert the physician to the possibility of histoplasmosis. Laboratory clues may include pancytopenia (anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia) as evidence of impaired bone marrow function or replacement of the marrow, elevated alkaline phosphatase level, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and electrolyte abnormalities suggestive of adrenal insufficiency. In some patients, adrenal hypofunction may not be clinically manifest until years later. Chest radiographs may be normal or show findings suggestive of earlier primary infection or of interstitial pneumonitis consistent with hematogenous spread of infection. In almost all instances, the syndrome occurs in young adults with no evidence of pulmonary or disseminated histoplasmosis. Laser photocoagulation appears to be the most beneficial therapeutic modality to prevent or reduce vision impairment. The diagnostic approach varies in part with the clinical syndrome under consideration. The histoplasmin skin test, although important in epidemiologic studies, is not recommended for diagnostic purposes, owing to the high positivity rate among persons residing in endemic areas. Although a titer of 1:32 or more or a fourfold rise in titer provides presumptive evidence of active infection, a negative or lower titer does not exclude histoplasmosis. Similarly, titers do not parallel disease activity, correlate with response to therapy, or predict outcome. Testing of serum by immunodiffusion to detect precipitin bands to M and H antigens appears to be a more specific but less sensitive serologic method than complement fixation. All antibody tests are associated with frequent false-positive reactions to Histoplasma antigens among patients with tuberculosis and other fungal diseases, especially blastomycosis and coccidioidomycosis. Antigen levels fall with treatment; consequently, this test is useful for both diagnosing and evaluating response to therapy. The diagnosis of primary pulmonary histoplasmosis should be suspected on the basis of clinical, radiographic, and epidemiologic clues. An elevated complement fixation titer and/or precipitin bands in serum provide presumptive evidence. Whereas sputum cultures are rarely positive (only 10 to 20%) in primary pulmonary disease, the likelihood of positive sputum cultures is significantly higher in chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis. Among patients with chronic disease, about 60% with marching thick-walled cavities have positive cultures, and a significant percentage of these also have positive smears of stained sputum.
During this time medications used for bipolar disorder cheap rocaltrol 0.25mcg fast delivery, the examiner can also assess mental status symptoms of pregnancy buy genuine rocaltrol, including speech treatment zinc toxicity discount rocaltrol 0.25 mcg on line, language medicine nobel prize 2015 buy rocaltrol 0.25mcg without prescription, fund of knowledge, and affect, and observe the patient for facial asymmetry, abnormalities of ocular movements, and an increase or a paucity of spontaneous movements as seen with movement disorders. Steer the patient away from discussions of previous diagnostic test results and of the opinions of previous caregivers. Take a careful medical history, medication history, psychiatric history, family history, and social and occupational history. Many neurologic illnesses are complications of underlying medical disorders or are due to adverse effects of drugs. For example, parkinsonism is a frequent complication of use of metoclopramide and most neuroleptic agents. A large number of neurologic disorders are hereditary, and a positive family history may establish the diagnosis in many instances. Occupation plays a major role in various neurologic disorders such as carpal tunnel syndrome (in computer keyboard operators), and 2008 peripheral neuropathy (caused by exposure to lead or other toxins). Patients with dementia or altered mental status are usually unable to provide exact details of the history, and a family member may provide key details needed to make an accurate diagnosis. This is especially true for patients with dementia and certain right hemispheric lesions with various agnosias (lack of awareness of disease) that may interfere with their ability to provide a cogent history. Surrogate historians also provide missing historical details for patients with episodic loss of consciousness, such as syncope and epilepsy. Summarizing the history is an effective way to ensure that all details were covered sufficiently to make a tentative diagnosis. Summarizing will also allow the physician to fill in historical gaps that may not have been apparent when the history was initially taken. In addition, the patient or surrogate may correct any historical misinformation at this time. Some patients have a specific diagnosis in mind that spurs them to seek medical attention. Examples of such disorders include headaches, seizures, developmental disorders, memory disorders, and behavioral diseases. Early-life events or long-standing processes such as head or spine trauma, unilateral hearing or visual loss, poor prowess in sports, poor performance in school, spinal curvature, or bone anomalies are easily overlooked but may point to the underlying disease process. Have the symptoms been progressive without remission, or have there been plateaus or periods of return to normal Cerebral mass lesions (tumor, subdural) tend to have a progressive but fluctuating course; seizures and migraine, an episodic course; strokes, an abrupt, ictal onset with worsening for 3-5 days followed by partial or complete recovery. Or is the process a disease of a system: B12 deficiency, myopathy, or polyneuropathy Traumatic injury inflicted by family members or other close contact with patients is usually difficult to detect by medical history and examination. Physically battered babies, abused children, battered women, and traumatized seniors are often unable or unwilling to complain of this cause or contribution to symptoms. The only method to prevent overlooking this frequent cause of common problems is systematic consideration of the possibility in every patient and awareness of the (often subtle) signs that suggest physical trauma: ecchymoses or fractures (often attributed to a logical cause), denial of expected symptoms, failure to keep appointments, and unexplained intensification of neurologic symptoms (headache, dizziness, ringing in the ears, blackouts). A host of neurologic disorders can be the result of the intentional ingestion of toxins. Consequently, physical signs and laboratory screening test results that give evidence of drug-related hepatic and other metabolic abnormalities (see the discussion of alcoholism) may point to a major underlying problem. Most neurologic diagnoses are arrived at by a careful, thorough history and an appropriately complete examination. However, the tempo of illness and the availability of life-saving treatment, that is only effective if administered within minutes of first evaluating a patient dictates rapid action in several specific circumstances. Coma, repetitive seizures, acute stroke, suspected meningitis and encephalitis, head and spine trauma, and acute spinal cord compression are each considered in chapters that follow. In each, diagnosis by clinical and laboratory assessment and urgent treatment must be instituted as soon as ventilation and cardiac status are stabilized. The complete neurologic examination of the child is much different from that of an elderly adult, and the examination of a patient with specific complaints will focus on findings pertinent to that patient. Thus, more detailed testing of cognition is indicated in patients with behavioral or memory disturbance and more detailed testing of sensation should be performed in patients with complaints of pain, numbness, or weakness. However, many tests of neurologic function are routinely indicated in all patients because they provide a baseline for future examination and because they are so frequently helpful in detecting unsuspected neurologic disease in apparently normal persons or in patients whose symptoms initially suggest disease outside the nervous system. It is particularly important to perform all routine tests in patients with abnormalities in one sphere of neurologic dysfunction; otherwise, erroneous localization of a lesion or disease process is likely.
Order 0.25 mcg rocaltrol fast delivery. 9 Early Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis.
Less common causes include chronic liver disease medicine 72 0.25 mcg rocaltrol with mastercard, inflammatory bowel disease medicine grapefruit interaction generic rocaltrol 0.25 mcg on line, and cyanotic heart disease medicine under tongue purchase rocaltrol 0.25 mcg online. There is also a hereditary form termed pachydermoperiostosis treatment plan for ptsd rocaltrol 0.25 mcg discount, with strong male 1559 predominance and a curious bimodal distribution of disease onset during the first year of life or the midteens. No satisfactory unifying theory of pathogenesis exists, although there is some evidence that platelet activation of endothelial cells, and excess platelet-derived growth factor and fibroblast growth factors, may cause the changes seen clinically. Successful treatment of the underlying disorder results in regression of the disorder. In fact, thoracotomy for cancer-causing pulmonary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy may result in a marked decrease in pain and swelling within 24 hours. Pamidronate and subcutaneous octreotide have been reported to reduce pain, which can be severe. The "sudden" onset of polyarthritis resembling rheumatoid arthritis in an older adult should prompt suspicion of an associated malignancy. Carcinoma polyarthritis may appear months before, or after, detection of malignancy of many types, particularly lung and breast. Its incidence is unknown; in one small series it was almost as common as carcinomatous hypertrophic osteoarthropathy and more common than cancer-related dermatomyositis. A report of foot and ankle fractures and their management in 18 patients with diabetes mellitus. Nevertheless, the specific characteristics of anxiety and depression have not been identified consistently on psychological testing, and it has been suggested that chronic pain and fatigue of any cause can engender anxiety and depression. These findings have been confirmed by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in a small number of patients. Other findings such as decreased regional cerebral blood flow have been cited as evidence for functional dysregulation of central pain pathways. Low-dose amitriptyline and fluoxetine are valuable for decreasing pain and improving sleep in some patients. Bursae are small, synovial-lined, fluid-filled sacs located between tendons and bones which serve to reduce friction between opposing muscles or tendons. Most bursae are present from birth; however, others form in response to repeated pressure. Of the approximately 80 bursae located on each side of the body, only a few are common sources of pain. The subdeltoid is the largest of the bursae around the shoulder (see Chapter 303); it is located between the deltoid muscle and the shoulder capsule and extends under the acromion. Acute inflammation of this or nearby bursae and tendons may be exceedingly painful, resulting in restricted shoulder movement and tenderness over the rotator cuff. Intrabursal injection of lidocaine is diagnostic and often curative; however, recurrences are common. Trochanteric bursitis is believed to occur as a result of chronic strain on weak quadricep muscles or overuse of hip and thigh muscles. Pain is often perceived to be in the lateral aspect of the thigh and the low back and is aggravated by abducting the affected leg and by lying on the affected side. Tendinous lesions include tenosynovitis, a lesion of the gliding surfaces of a tendon and its sheath; tendinitis, painful scarring within a tendon; and trigger lesions, which are localized enlargements of the tendon that engage a constricted part of the sheath (as in "trigger finger"). Flexor digital tenosynovitis may cause pain in the metacarpophalangeal or proximal interphalangeal joints. Tendinous lesions are common, occurring in many areas of the musculoskeletal system. The symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome are paresthesias and pain in the palmar side of the first three fingers and at times the radial half of the fourth finger; the pain may radiate proximally to the shoulder, creating confusion with a cervical disk syndrome. Physical findings include sensory loss, weakness on abduction and opposition of the thumb, and atrophy of the thenar eminence. Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by an array of conditions that result in pressure on the median nerve as it passes through the bony flexor compartment of the wrist. A tear or area of degeneration most often occurs at the origin of the common extensor tendon from the lateral humoral epicondyle; much less frequently, the tear is in the muscle belly. Treatment includes exercise of wrist extensor muscles, injection of triamcinolone into the painful scar, manipulation, or partial tenotomy. Pain is usually localized to the inner side of the elbow and is produced by resisted flexion of the wrist.
When rat control programs are instituted medications gerd discount rocaltrol online mastercard, appropriate insecticides should be simultaneously used to prevent the fleas from seeking humans for feeding as the rat population is decreased medications that cause constipation discount rocaltrol 0.25mcg with mastercard. It is a sometimes fatal systemic infection manifested by fever treatment plant purchase rocaltrol online pills, severe headache medications kidney failure generic 0.25 mcg rocaltrol amex, rash, and other organ disease caused by the vasculitis induced by Rickettsia rickettsii. The organism is usually transmitted to humans from animal reservoirs by a tick bite. In human infections the rickettsiae invade and multiply within endothelial cells of arteries and veins. Attempts to correlate virulence with structural components in the polysaccharide portion of the cell wall have been unsuccessful. This disease was named for the geographic site of its original discovery; the causative agent was named for the discoverer, Howard T. By the 1940s the disease had become more common on the East Coast than in the West. Serologic surveys in children and adults in North Carolina, the state with the highest number of reported cases, demonstrate that subclinical infections occur. Ninety per cent of reported cases occur between April 1 and September 30, with two thirds in May, June, and July. Ninety per cent of patients give a history of a tick bite or attachment or of having been in a tick-infested area 14 days before onset of illness. Increases in reported cases of Rocky Mountain spotted fever may reflect heightened awareness and surveillance for emerging tick-borne diseases. Probably fewer than 10 organisms injected intradermally are sufficient to induce disease. Several species of ticks are commonly involved in transmission of disease: Dermacentor andersoni, the wood tick, in the Rocky Mountain states; D. These ticks feed on small mammals such as ground squirrels and rabbits as well as on larger animals such as bear and deer. Laboratory-acquired infections have occurred in persons exposed to droplets from accidental generation of aerosols from solutions of the organism. However, even in circumstances conducive to airborne transmission, person-to-person transmission does not occur. The basis of the pathologic changes in this disease, as in other rickettsial infections, is the inflammatory response stimulated by the irreparable damage of the endothelial cells. This infectious process results in changes in the endoplasmic reticulum, the outer nuclear membrane, and the plasma membrane. Also, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 production is increased; these and other substances. In patients dying within 3 to 5 days of onset of disease, significant coagulation abnormalities are present. Microinfarcts result from occlusions of small vessels, and edema and hemorrhages occur secondary to increased permeability of the vasculature. Such lesions can be found in the heart, kidneys, adrenals, lungs, brain, skin, spleen, and subcutaneous tissues. The rash is thought to result from the vasculitis and the associated permeability changes. Petechial lesions are caused by microhemorrhages secondary to the vasculitis and thrombocytopenia. These patients have severe hemolytic reactions and significant thrombotic lesions in the glomeruli, resulting in oliguria. The incubation period of naturally acquired disease has a range of 2 to 14 days with an average of 7 days. The onset of disease in the typical case is sudden, with a severe headache, often retrobulbar in location, chills, fever, myalgia, malaise, nausea and vomiting, conjunctival injection, and photophobia. The duration of fever in untreated cases is about 2 weeks, but recovery from the debilitating effects of the disease requires several additional weeks. Rash appears in 80 to 90% of patients-usually on the third or fourth day of fever, rarely after 5 or more days.