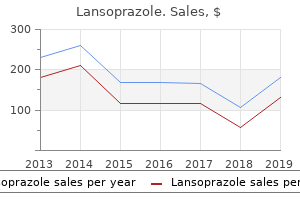
"Cheap lansoprazole 30mg with visa, gastritis diet ÿíäåõ".
By: R. Tyler, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Professor, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine
The extended family is however becoming weaker because everyone gastritis zungenbelag lansoprazole 30mg for sale, even those considered better off chronic gastritis x ray lansoprazole 30 mg online, is not in a position to spare food or money acute gastritis definition cheap 30 mg lansoprazole. A number of methods to alleviate poverty are readily available gastritis diet in pregnancy buy cheap lansoprazole 15mg, including the deployment of a community and family safety net, the use of self-help and mutual help schemes and agreements, loans, revolving funds and other time-honoured approaches (Khumalo, 2006). Among the factors responsible for the high levels of poverty is the persistent drought that has caused famine in many rural communities, especially in the eastern lowveld and Lubombo plateau. In addition, the loss of income through retrenchments and rising general unemployment contributed to the lack of access to productive resources by the poor. High levels of income inequality have entailed that a disproportionate share of the limited resources is captured by rich people. Consequently poor people have none or limited resources to fight or cope with the pandemic. Lastly, the pandemic has intensified poverty due to the loss of earnings from breadwinners in families (Ibid). The ills that have been created by poverty are numerous and have weakened the good practices that were created by the traditional social networks. Individuals and families are now entirely dependent on selling their labour or engaging in income generating activities where possible. The community as a safety net Communities have a social responsibility towards the welfare of their members. In the past, traditional cultural practices ensured that a social safety net was provided to needy people (Khumalo, 2006), meaning that mechanisms of sharing resources were in place. The community donated surplus food to the chief indlunkhulu who then catered to the needy in the community. Due to recent trends with urbanisation, migration and poor crop yields, the viability of this system was in doubt until recent measures enacted by government and civil society. In some communities residents consequently took most of the maize for their own consumption, depriving the vulnerable children who were the intended beneficiaries. Their efforts have re-activated the traditional practices of providing a safety net to needy people in the community. Orphans and vulnerable children are also taken care of through programmes that have adopted traditional concepts like gogo centres. Traditionally, grandmothers acted like a mother hen, sheltering all those who required assistance in families, hence the term gogo centres. Urbanisation and modernisation have shifted all responsibility for service and care from communities to institutions like schools, hospitals and other service providers who are doing it for commercial gain. The challenge is the decline in the traditional ways of assisting each other, especially helping disadvantaged or weak people. Communities are already struggling to make ends meet and poverty is widespread, with a prolonged drought that shows no signs of immediate relief. Nonetheless, the government is making inroads in the finalisation of policies that will hopefully alleviate poverty and the food security crisis. The apex of this traditional leadership structure is the King, who rules, with chiefs at the lower traditional level. In 2000 he declared a five-year period of girls observing umcwasho, a cultural rite promoting abstinence and condemning early sexual debut in adolescent youths. The Queen Mother also joined the fight, using cultural prevention methods through Khulisa Umntfwana, a project with the mission to raise children with good morals. In addition, the government intensified and scaled up the national response, as discussed in chapter five. Kingship and rank are central to the Swazi socio-political system, with royalty and tradition as the basis upon which authority has been maintained (Forster and Nsibande, 2000). The royal family have lived to the premise that tradition is a living thing, which has to be made contemporary to each generation. The King and the royal family have adopted a modern lifestyle that is mixed with traditional practices, which are becoming more seasonal than defining their entire lifestyle. Contemporary Swaziland is however faced with the challenge of the gatekeepers of tradition, who are trying hard to "lock" culture as a permanently defined social construct. The realities of traditions and behavioural practices are continually evolving, making culture as a living thing inescapable. This calls for the renewal of tradition to make it contemporary to the generation of today. Indlunkhulu (Chiefdom) the chief or umphakatsi is the traditional leadership of a community with a hierarchy of authority.
Diseases
- Ectropion inferior cleft lip and or palate
- Entomophthoramycosis
- Hypoadrenalism
- Say Carpenter syndrome
- Glucocorticoid sensitive hypertension
- Non-small cell lung cancer
- Spastic paraplegia neuropathy poikiloderma
- Adducted thumbs Dundar type
Eye drops are generally instilled into the lower conjunctival sac which is accessed by gently pulling down the lower eyelid to form a pocket into which one drop is instilled gastritis diet of hope purchase lansoprazole no prescription. The eye should be kept closed for as long as possible after application gastritis best diet purchase discount lansoprazole online, preferably 1Â2 minutes gastritis diet quotes buy lansoprazole with visa. A small amount of eye ointment is applied similarly; the ointment melts rapidly and blinking helps to spread it diet for gastritis and duodenitis discount lansoprazole 15 mg overnight delivery. When two different eye drops are required at the same time, dilution and overflow may occur if one immediately follows the other; an interval of at least five minutes should therefore be allowed between the two applications. Systemic absorption, which may occur after topical application of eye drops, can be minimized by using the finger to compress the lacrimal sac at the medial canthus for at least one minute after instillation of the drops. Performance of skilled tasks Application of eye preparations may cause blurring of vision which is generally transient; patients should be advised not to carry out skilled tasks, such as operating machinery or driving, until their vision has cleared. However, in some cases, for example, in gonococcal conjunctivitis, both topical and systemic anti-infective treatment may be necessary. Blepharitis and conjunctivitis are often caused by staphylococcus, while keratitis and endophthalmitis may be bacterial, viral, or fungal. Although most cases of acute bacterial conjunctivitis may resolve spontaneously, anti-infective treatment shortens the infectious process and prevents complications. Acute infective conjunctivitis is treated with antibacterial eye drops by day and eye ointment applied at night. Ophthalmological preparations is an antiviral used in the treatment of keratitis due to herpes simplex virus. Gentamicin is a broad-spectrum bactericidal aminoglycoside antibiotic with particular activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria gonorrhoea and other bacteria that may be implicated in blepharitis or conjunctivitis. Tetracycline is a broad spectrum antibiotic with activity against many Grampositive and Gram-negative bacteria including N. Ophthalmic tetracycline is used in blepharitis, conjunctivitis, and keratitis produced by susceptible bacteria. Tetracycline is also used in the treatment of trachoma caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and in the prophylaxis of neonatal conjunctivitis (ophthalmia neonatorum) caused by N. Uses: keratitis caused by herpes simplex; systemic herpes simplex infections (section 6. Adverse effects: local irritation including transient mild stinging, inflammation; superficial punctuate keratopathy reported; very rarely hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to aminoglycoside group of antibiotics Precautions: prolonged use may lead to skin sensitization and emergence of resistant organisms including fungi; discontinue if there is purulent discharge, inflammation or exacerbation of pain. Anti-inflammatory agents Ophthalmic corticosteroids should only be used under supervision of an ophthalmologist as inappropriate use is potentially blinding. Dangers include the development of open-angle glaucoma (chronic simple glaucoma) and cataracts, and the aggravation of a simple herpes simplex epithelial lesions into extensive corneal ulcers and subsequent permanent corneal scarring, with possible damage to vision and even loss of the eye. Corticosteroids such as prednisolone are useful in the treatment of inflammatory eye conditions including uveitis and scleritis. Before administration of an ophthalmic corticosteroid, the possibility of bacterial, viral, or fungal infection should be excluded. Treatment should be with the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible time; if long-term therapy (more than 6 weeks) is unavoidable, withdrawal of an ophthalmic corticosteroid should be gradual to avoid relapse. Precautions: cataract; corneal thinning, corneal or conjunctival infection; discontinue treatment if no improvement within 7 days; risk of adrenal suppression after prolonged use in infants. Adverse effects: secondary ocular infection; impaired corneal healing (due to corneal thinning), optic nerve damage, cataract; glaucoma, mydriasis, ptosis, epithelial punctate keratitis, delayed hypersensitivity reactions including burning, and stinging. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to ester-type local anaesthetics; eye inflammation or infection. Precautions: avoid prolonged use (risk of severe keratitis, permanent corneal opacification, scarring, and delayed corneal healing); protect eye from dust and bacterial contamination until sensation is fully restored. The rise in pressure is almost always due to reduced outflow of aqueous humour, the inflow remaining constant. The most common condition is chronic open-angle glaucoma (chronic simple glaucoma) in which the intraocular pressure increases gradually and the condition is usually asymptomatic until well advanced. In contrast, angle-closure glaucoma (closed-angle glaucoma) usually occurs as an acute emergency resulting from a rapid rise in intraocular pressure; if treatment is delayed, chronic angle-closure glaucoma may develop. In ocular hypertension, intraocular pressure is raised without signs of optic nerve damage. Ophthalmological preparations Drugs used in the treatment of glaucoma lower the intraocular pressure by a variety of mechanisms including reducing the secretion of aqueous humour by the ciliary body, or increasing the outflow of the aqueous humour by the opening of the trabecular network.
Purchase generic lansoprazole. 5 Best Foods to Heal Leaky Gut.
Understanding decreases anxiety regarding intestinal function and enhances independence in self-care gastritis diet ýëüäîðàäî discount lansoprazole 15mg without a prescription. Monitoring of clinical symptoms and serum blood levels is indicated because of altered drug absorption gastritis diet bland lansoprazole 30mg line, requiring periodic dosage adjustments gastritis pdf discount lansoprazole 30mg overnight delivery. Discuss effect of medications on effluent gastritis diet ginger order lansoprazole 15mg otc, that is, changes in color, odor, and consistency of stool, and need to observe for drug residue indicating incomplete absorption. Stress necessity of close monitoring of chronic health conditions requiring routine oral medications. Obstruction, along with continued secretion of mucus, causes the wall of the appendix to become distended. Blood supply to the wall of the appendix is reduced, causing ischemia and accumulation of toxins. Wall of the appendix starts to break down, and normal bacteria found in the gut attacks the decaying appendix. Individual may experience spon-taneous recovery from inflammation at this stage or it may progress. Peritoneal fold attaching the appendix to the ileum (mesoappendix) often becomes inflamed. Obstruction of appendix lumen causes it to become vulnerable to invasion of bacteria normally found in the gut. Peak incidence in individuals in their late teens and early 20s; occurs more commonly in men than in women. Procedures-Inflamed appendix may be surgically removed using an open incision or using a laparoscopic approach with laser. Presence of multiple adhesions, retroperitoneal positioning of the appendix, or the likelihood of rupture necessitates an open or traditional procedure. Laparoscopic procedure results in significantly less postoperative pain, lower wound infection rate, and faster return to normal activities. Morbidity: Approximately 250,000 cases are reported annually in the United States. G L O S S A R Y Abcess: Collection of pus in any part of the body that is surrounded by inflammation and infection. Peritonitis: Inflammation of the peritoneum, the tissue layer of cells lining the inner wall of the abdomen and pelvis. Rebound tenderness: Pain felt when a hand pressing on the abdomen is suddenly released; a symptom of peritoneal inflammation. Gold standard test for differentiation of appendicitis from other causes of abdominal pain, such as perforating ulcer, cholecystitis, and reproductive organ infections, or to localize drainable abscesses. May reveal hardened bit of fecal material in appendix (fecalith) and localized ileus. Provide information about surgical procedure, prognosis, treatment needs, and potential complications. Surgical procedure, prognosis, therapeutic regimen, and possible complications understood. Note characteristics of drainage from wound or drains (if inserted) and presence of erythema. Provides for early detection of developing infectious process and monitors resolution of preexisting peritonitis. Note onset of fever, chills, diaphoresis, changes in mentation, and reports of increasing abdominal pain. Antibiotics given before appendectomy are primarily for prophylaxis of wound infection and are not usually continued postoperatively. Therapeutic antibiotics are administered if the appendix is ruptured or abscessed, or peritonitis has developed. Monitor intake and output (I&O); note urine color and concentration and specific gravity. Provide clear liquids in small amounts when oral intake is resumed, and progress diet as tolerated.
Honghua (Safflower). Lansoprazole.
- Dosing considerations for Safflower.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Reducing LDL cholesterol.
- How does Safflower work?
- Fever, tumors, coughs, bronchial conditions, blood circulation disorders, pain, menstrual disorders, chest pain, traumatic injuries, constipation, inducing sweating, causing abortion, and other uses.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96138