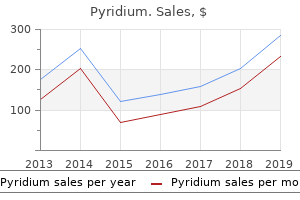
"Buy 200 mg pyridium free shipping, gastritis diet 6 months".
By: D. Myxir, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Professor, A.T. Still University School of Osteopathic Medicine in Arizona
Interventions should be provided by trained interventionists in either individual or group sessions (21) gastritis vitamins buy discount pyridium 200 mg online. Some commercial and proprietary weight loss programs have shown promising weight loss results (22) gastritis diet mayo order pyridium with mastercard. Weight regain following the cessation of very low-calorie diets is greater than following intensive behavioral lifestyle interventions unless a long-term comprehensive weight loss maintenance program is provided (23 gastritis diet natural treatment cheap 200mg pyridium otc,24) gastritis diet ãîãëå safe pyridium 200mg. E Whenever possible, minimize the medications for comorbid conditions that are associated with weight gain. Potential benefits must be weighed against the potential risks of the medications. A Antihyperglycemic Therapy When evaluating pharmacological treatments for overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes, providers should first consider their choice of glucose-lowering medications. Whenever possible, medications should be chosen to promote weight loss or to be weight neutral. Unlike these agents, insulin secretagogues, thiazolidinediones, and insulin have often been associated with weight gain (see Section 8 "Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment"). Concomitant Medications low-calorie diets and to reinforce lifestyle changes including physical activity. Providers should be knowledgeable about the product label and should balance the potential benefits of successful weight loss against the potential risks of the medication for each patient. Assessing Efficacy and Safety c Efficacy and safety should be assessed at least monthly for the first 3 months of treatment. In general, pharmacological treatment of obesity has been limited by low adherence, modest efficacy, adverse effects, and weight regain after medication cessation (25). C People presenting for metabolic surgery should receive a comprehensive mental health assessment. B Surgery should be postponed in patients with histories of alcohol or substance abuse, significant depression, suicidal ideation, or other mental health conditions until these conditions have been fully addressed. E People who undergo metabolic surgery should be evaluated to assess the need for ongoing mental health services to help them adjust to medical and psychosocial changes after surgery. Medications approved for long-term weight loss and weight loss maintenance and their advantages and disadvantages are summarized in Table 7. B Metabolic surgery should be performed in high-volume centers with multidisciplinary teams that understand and are experienced in the management of diabetes and gastrointestinal surgery. Cohort studies attempting to match surgical and nonsurgical subjects suggest that the procedure may reduce longer-term mortality (31). Women in their reproductive years must be cautioned to use a reliable method of contraception. Refer to the medication package inserts for full information about adverse effects, cautions, and contraindications. In clinical trials in obese patients with diabetes, hypoglycemia and abdominal distension were also observed. Please refer to the American Diabetes Association consensus report "Metabolic Surgery in the Treatment Algorithm for Type 2 Diabetes: A Joint Statement by International Diabetes Organizations" for a thorough review (29).
Blood glucose levels that are persistently above this level may require alterations in diet or a change in medications that cause hyperglycemia symptoms of gastritis flare up discount 200 mg pyridium visa. Previously gastritis diet natural treatment purchase pyridium on line amex, hypoglycemia in hospitalized patients has been defined as blood glucose gastritis recovery effective pyridium 200 mg,70 mg/dL (3 gastritis forum order pyridium 200mg on line. A blood glucose level of #70 mg/dL is considered an alert value and may be used as a threshold for further titration of insulin regimens. More frequent blood glucose testing ranging from every 30 min to every 2 h is required for patients receiving intravenous insulin. Safety standards should be established for blood glucose monitoring that prohibit the sharing of fingerstick lancing devices, lancets, and needles (17). Point-of-Care Meters Appropriately trained specialists or specialty teams may reduce length of stay, improve glycemic control, and improve outcomes, but studies are few. Details of team formation are available from the Society of Hospital Medicine and the Joint Commission standards for programs. Quality Assurance Standards Even the best orders may not be carried out in a way that improves quality, nor are they automatically updated when new evidence arises. To this end, the Joint Commission has an accreditation program for the hospital care of diabetes (12), and the Society of Hospital Medicine has a workbook for program development (13). This evidence established new standards: insulin therapy should be initiated for treatment of persistent hyperglycemia starting at a threshold $180 mg/dL (10. Conversely, higher glucose ranges may be acceptable in terminally ill patients, in patients with severe comorbidities, and in inpatient care settings where frequent glucose monitoring or close nursing supervision is not feasible. Significant discrepancies between capillary, venous, and arterial plasma samples have been observed in patients with low or high hemoglobin concentrations and with hypoperfusion. However, in certain circumstances, it may be appropriate to continue home regimens including oral antihyperglycemic medications (21). Prolonged sole use of sliding scale insulin in the inpatient hospital setting is strongly discouraged (2,11). Therefore, premixed insulin regimens are not routinely recommended for in hospital use. Type 1 Diabetes In the critical care setting, continuous intravenous insulin infusion has been shown to be the best method for achieving glycemic targets. Intravenous insulin infusions should be administered based on validated written or computerized protocols that allow for predefined adjustments in the infusion rate, accounting for glycemic fluctuations and insulin dose (2). Typically basal insulin dosing schemes are based on body weight, with some evidence that patients with renal insufficiency should be treated with lower doses (25). Transitioning Intravenous to Subcutaneous Insulin of hypoglycemia compared with a basalbolus regimen (30). A review of antihyperglycemic medications concluded that glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists show promise in the inpatient setting (32); however, proof of safety and efficacy await the results of randomized controlled trials (33). Moreover, the gastrointestinal symptoms associated with the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists may be problematic in the inpatinet setting. Regimens using insulin analogs and human insulin result in similar glycemic control in the hospital setting (22). If oral intake is poor, a safer procedure is to administer the rapid-acting insulin immediately after the patient eats or to count the carbohydrates and cover the amount ingested (22). A randomized controlled trial has shown that basal-bolus treatment improved When discontinuing intravenous insulin, a transition protocol is associated with less morbidity and lower costs of care (26) and is therefore recommended. For patients continuing regimens with concentrated insulin in the inpatient setting, it is important to ensure the correct dosing by utilizing an individual pen and cartrige for each patient, meticulous pharmacist supervision of the dose administered, or other means (28,29).
If it is not clear from the available records what the change of diagnosis represents gastritis symptoms weight loss generic pyridium 200mg, the rating agency shall return the report to the examiner for a determination gastritis etiology buy generic pyridium on-line. However gastritis diet during pregnancy buy pyridium canada, disability resulting from a mental disorder that is superimposed upon mental retardation or a personality disorder may be service-connected gastritis diet avocado buy 200mg pyridium with amex. If a mental disorder has been assigned a total evaluation due to a continuous period of hospitalization lasting six months or more, the rating agency shall continue the total evaluation indefinitely and schedule a mandatory examination six months after the veteran is discharged or released to nonbed care. Occupational and social impairment, with deficiencies in most areas, such as work, school, family relations, judgment, thinking, or mood, due to such symptoms as: suicidal ideation; obsessional rituals which interfere with routine activities; speech intermittently illogical, obscure, or irrelevant; near-continuous panic or depression affecting the ability to function independently, appropriately and effectively; impaired impulse control (such as unprovoked irritability with periods of violence); spatial disorientation; neglect of personal appearance and hygiene; difficulty in adapting to stressful circumstances (including work or a worklike setting); inability to establish and maintain effective relationships. Occupational and social impairment with reduced reliability and productivity due to such symptoms as: flattened affect; circumstantial, circumlocutory, or stereotyped speech; panic attacks more than once a week; difficulty in understanding complex commands; impairment of short- and long-term memory. Occupational and social impairment with occasional decrease in work efficiency and intermittent periods of inability to perform occupational tasks (although generally functioning satisfactorily, with routine behavior, self-care, and conversation normal), due to such symptoms as: depressed mood, anxiety, suspiciousness, panic attacks (weekly or less often), chronic sleep impairment, mild memory loss (such as forgetting names, directions, recent events). Occupational and social impairment due to mild or transient symptoms which decrease work efficiency and ability to perform occupational tasks only during periods of significant stress, or; symptoms controlled by continuous medication. A mental condition has been formally diagnosed, but symptoms are not severe enough either to interfere with occupational and social functioning or to require continuous medication. Self-induced weight loss to less than 85 percent of expected minimum weight with incapacitating episodes of six or more weeks total duration per year. Self-induced weight loss to less than 85 percent of expected minimum weight with incapacitating episodes of more than two but less than six weeks total duration per year. Binge eating followed by self-induced vomiting or other measures to prevent weight gain, or resistance to weight gain even when below expected minimum weight, with diagnosis of an eating disorder and incapacitating episodes of up to two weeks total duration per year. Binge eating followed by self-induced vomiting or other measures to prevent weight gain, or resistance to weight gain even when below expected minimum weight, with diagnosis of an eating disorder but without incapacitating episodes. All upper and lower posterior teeth missing All upper and lower anterior teeth missing. Rating 9900 Maxilla or mandible, chronic osteomyelitis or osteoradionecrosis of: Rate as osteomyelitis, chronic under diagnostic code 5000. Diagnostic Code 5297-(Removal of one rib) ``or resection of 2 or more'; August 23, 1948. Diagnostic Code 6076-60%: Vision 1 eye 15/ 200 and other eye 20/100; August 23, 1948. Diagnostic Code 6081-Words ``unilateral', ``minimal' and all of Note; March 10, 1976. Diagnostic Code 6350; 80% Evaluation and Criterion for 60% and 30% Evaluations; March 10, 1976. Diagnostic Code 7000-100 percent inactive ``with signs of congestive failure upon any exertion beyond rest in bed' revoked; Diagnostic Code 7005-80 percent revoked; Diagnostic Code 7007-80 percent revoked; Diagnostic Code 7015-100 percent Evaluation. Diagnostic Code 5002-100 percent, 60 percent, 40 percent, 20 percent; March 1, 1963. Diagnostic Code 7121-100 percent Criterion and Evaluation and 60 percent Criterion; March 10, 1976. Diagnostic Code 7312-70% Evaluation and 50% Evaluation and Criterion; March 10, 1976. Diagnostic Code 7911-Evaluations and Note; March 1, 1963; 40% and 20% Evaluations; August 13, 1981.
Oral amiodarone increases the efficacy of direct-current cardioversion in restoration of sinus rhythm in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation gastritis symptoms natural remedies buy discount pyridium online. Effects of a high dose intravenous bolus amiodarone in patients with atrial fibrillation and a rapid ventricular rate gastritis diet list of foods to avoid pyridium 200mg overnight delivery. Intravenous amiodarone bolus immediately controls heart rate in patients with atrial fibrillation accompanied by severe congestive heart failure gastritis diet 360 cheap pyridium online mastercard. Digoxin use and subsequent outcomes among patients in a contemporary atrial fibrillation cohort gastritis diet à10 purchase pyridium 200mg mastercard. Increased mortality associated with digoxin in contemporary patients with atrial fibrillation. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: the Euro Heart Survey on atrial fibrillation. Meta-analysis: antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Left atrial appendage closure as an alternative to warfarin for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: a patient-level meta-analysis. Inducible myocardial ischemia and outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease and left ventricular dysfunction. Heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the challenges facing physicians and health services. Carvedilol alone or in combination with digoxin for the management of atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with concomitant left ventricular impairment: a systematic review of efficacy and effect on ejection fraction. Catheter ablation and antiarrhythmic drug therapy as first- or second-line therapy in the management of atrial fibrillation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Antiarrhythmics for maintaining sinus rhythm after cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. A multicentre, randomized trial on the benefit/risk profile of amiodarone, flecainide and propafenone in patients with cardiac disease and complex ventricular arrhythmias. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Risk of major bleeding in different indications for new oral anticoagulants: insights from a meta-analysis of approved dosages from 50 randomized trials. New oral anticoagulants in elderly adults: evidence from a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Updated European Heart Rhythm Association practical guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist anticoagulants in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Iron deficiency and health-related quality of life in chronic heart failure: results from a multicenter European study. Noncardiac comorbidity increases preventable hospitalizations and mortality among Medicare beneficiaries with chronic heart failure. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, Available at /ginasthma. Cardiovascular side effects of cancer therapies: a position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Effect of free fatty acid inhibition on silent and symptomatic myocardial ischemia in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease. Trimetazidine improves left ventricular function and quality of life in elderly patients with coronary artery disease. Trimetazidine, a metabolic modulator, has cardiac and extracardiac benefits in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Effect of trimetazidine on quality of life in elderly patients with ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Trimetazidine improves left ventricular function in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease: a doubleblind placebo-controlled study.
Discount pyridium 200mg online. Symptoms of Gastritis : Causes and Treatment.